Thalassemia is a genetic form of anemia that affects children of both sexes , most of them are from the Mediterranean regions , Africa and Asia .
Its symptoms appear at an early age, and may be delayed until adolescence.
Thalassemia in its simplified form represents a quantitative disorder of hemoglobin i.e a decrease in the amount of protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the cells of the body , which explains why its symptoms are similar to those of anemia: Paleness, tiredness, short breath ..
Sometimes parents notice a change of the skin color to yellow, or what is known as jaundice, and the color of urine to dark .
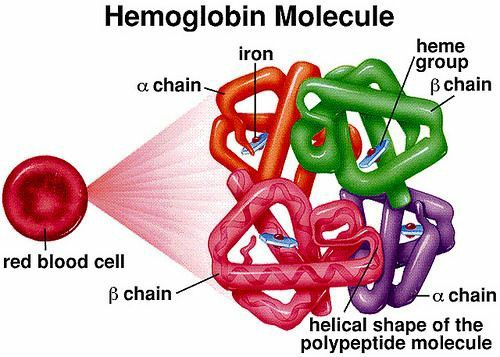
hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells, composed of 2 types of peptide chains: Alpha and beta and thus we can divide thalassemia into 2 large groups:
Alpha thalassemia: decrease or absence of the alpha chain of hemoglobin.
Beta thalassemia: reduction or absence of the beta chain .
Alpha-thalassemia is more common in the black population (25% of this population carries at least one copy of the defective gene);
Beta-thalassemia, on the other hand, is more common in people from around the Mediterranean and Southeast Asia.
Children inherit this gene from one or both parents :
If it is inherited from both parents, the child will have Major Thalassemia and if it is inherited from only one parent, the child will have Minor Thalassemia which is asymptomatic , there is an intermediate form, less severe than the major one but still symptomatic and which is generally discovered later.
The major beta thalassemia is also called Cooley disease , its symptoms appear since day 1 , the child has a typical face and severe complications: bone malformations , hypogonadism, delayed puberty, gallstones and hypersplenism.
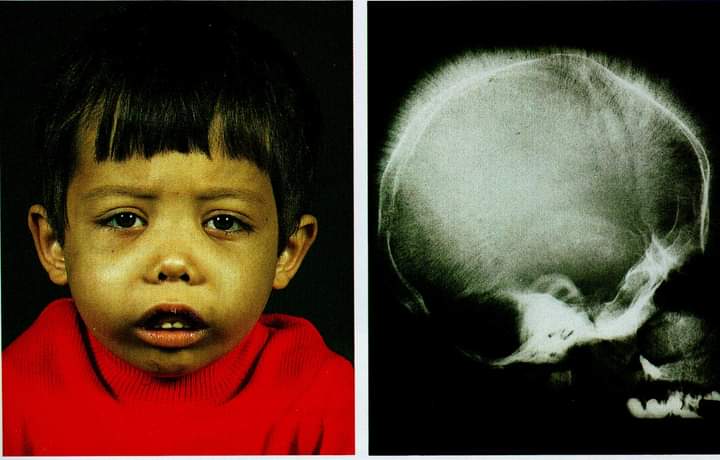
Complications of Thalassemia :
high risk of infectious diseases, growth troubles and heart complications.
When should you seek medical help? And can this disease be prevented?
In most cases, you cannot prevent Thalassemia.
If you have Thalassemia, or carry its genes, there will always be a chance for the next generation to have it aswell .
When should you consult a doctor ? :
1. If your child shows symptoms of anemia.
2. If you have a family history of Thalassemia, you should get tested to see if you have it too.
The treatment depends on the type and severity of its symptoms.
The treatment of moderate to severe Thalassemia includes : Blood transfusion , folic acid supplement , stem cell transplant and complications treatment.
Finally, it is always a good idea to speak with a doctor and a genetic counselor if there are genetic factors in the family history before having children.