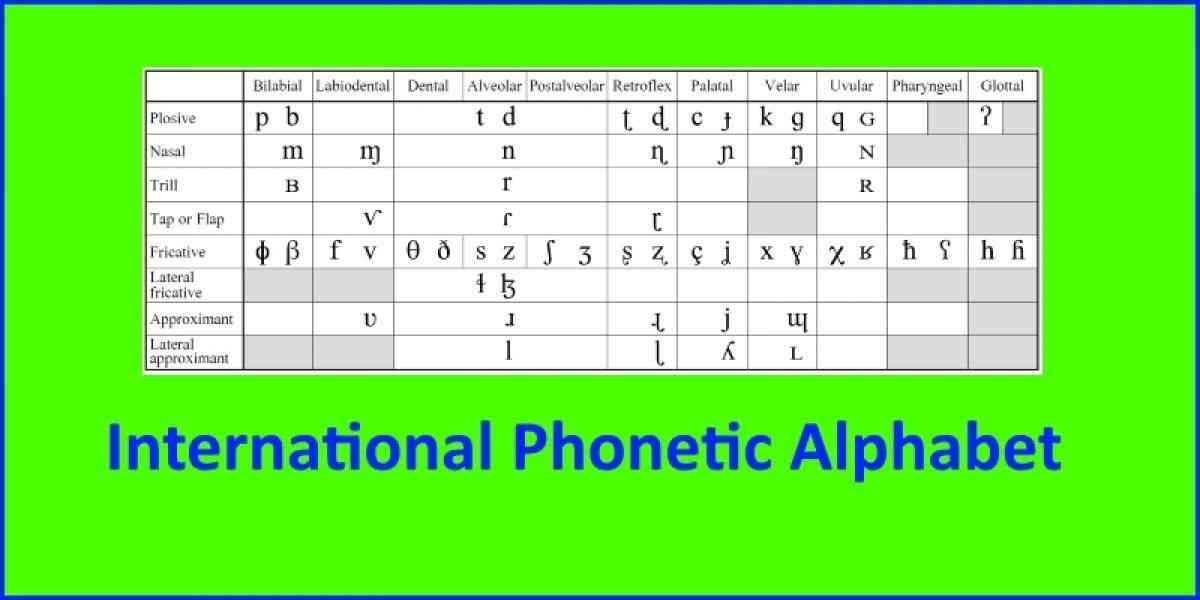
The IPA is a standard system used in phonetic representations of possible sounds in every language in the world. The main objective of the IPA system has been to promote the scientific study of phonetics in general and to expand the use of the IPA alphabet. IPA are a series of specific signs. Each sign represents a sound that are used for phonetic transcriptions in most languages in the world.

The IPA is a standard system used in phonetic representations of possible sounds in every language in the world. The main objective of the IPA system has been to promote the scientific study of phonetics in general and to expand the use of the IPA alphabet. IPA are a series of specific signs.Each sign represents a sound that are used for phonetic transcriptions in most languages in the world.
The IPA was published at the end of the last century by the "International Fonetica Asoation" and was perfected and improved with progressive contributions to become the current alpha-baltic system. Its history dates back to 1878 when a group of French and British masters led by the French linguist Paul Passy decided and formed what would come to be known as the International Phonetic Association which in French was "L'Association Phonétique Internationale".
The original intention of the IPA was to create an innoating group of symbols that had different values for each language. Finally, it was decided to create a single alphabet for all languages. The first official version of the International Phonetic Association was released in 1888, 2 years after the International Phonetic Association was phorame, based on the alphabet of Henry Sweet, which in turn formed the phonypic alphabet of Isaac Pitman and Alexander John Ellis. The IPA since it was created, the organization of vowels and consonants in the Fonetica International Association have generally been the same.
However, the alphabet has undergone quite a few modifications in each language.
The "IPA Kiel Convention" in 1989 made many changes to the previous version of 1832. Then, minor modifications were made taking place in 1993, with additions of the central middle vowel and eliminating symbols for deaf implsives. The alphabet was finally modified at the general level in May 2005 when the symbol for the vibrant simple lipdental was added.

IPA is mainly used in radio transmissions to ensure proper interpretation of messages. When transmissions are not generally optimal, you need to spell out what is said by some international code that can be understood by any recipient transmission. The alphabet associates keywords with each letter; in this way the system can be used in maritime transmissions in the same way, aeronautical or terrestrial and is contemplated in the international code of signals that also includes the morse code and signals with flags.
The IPA also provides a standardized, unique and accurate way of representing the sounds of any oral language and is used by millions of linguists around the world, speech therapists and therapists, foreign language teachers, lexicographs and professional translators. Since its basic form since 2005: the IPA has approximately 107 base symbols and 55 modifiers.
The symbols of this alphabetic system have been incorporated into the standard spellings of many languages, notably within the African continent, but in other regions of the same way. Including: Hausa, Fula, Akan, Gbe Languages and Mandinga Languages. The international phonetic alphabet divides all its letter symbols into 3 categories called:
- pulmonic consonants
- non-pulmonic consonants
- vowels
Each character is assigned a number, preventing confusion between similar letters such as: (a. and s).
Another example is the impression of many manuscripts, many categories of sounds assigned to them various ranges of numbers.

Sounds and Symbols
This International Phone Alphabet was based on the letters of the Latin alphabet.
Using few non-Latin forms as possible. The association created the AFI so that the sounds of most of the consonants taken from the Latin alphabet corresponded to an international use that was accessible to many speakers.
These consonants are:
- b
- d
- f
- g
- k
- l
- m
- n
- p
- p
- s
- t
- v
- z
The other consonants of the Latin alphabet are: - c
- h
- j
- q
- r
- w
- x
And they correspond to sounds that are represented in other languages; vowels of the Latin alphabet such as "a,e,i,o,u" correspond to the healthy values of the Latin "i" that is like the vowel in machine:
- u / example: rule, etc.
Other letters differ in English but use these values in other European languages in the same way as in:
- j
- r
Then the inventory of symbols was expanded using different forms, diacritic signs and rotation of capital or italics. There are also many derivatives of the Greek alphabet such as:
- β
- ɣ
- ɛ
- θ
- ɸ
- χ
- ʋ
Although many of these values that are healthy can differentiate. For example, "ʋ" is a vowel in Greek, but a single indirectly consonant that is related in the IPA.
Healthy values in modified Latin letters can change and often derive from those of the original letters.The letters with a hook of the coatings in the background are those that represent retroflex consonants, and small capitals generally represent uvular consonants. Certain kinds of modification to the shape of a letter generally correspond to certain kinds of modification to a sound.

Language Word Pronunciation
- Spanish: Mexico [ˈmexiko]
- Spanish: Oaxaca [gwaˈxaka]
- English: Friend [fɹɛnd]
- English Island [ˈaɪ̯lənd]
- French: Mademoiselle [madmwaˈzɛl]
- Chinese: [ni˧˥xaʊ˨˩˦]
- Italian: Pizza [ˈpit̪͡s̪ːä]

The phonetic alphabet is called "phonetic alphabet" because of the variety of sets of symbols that are used to classify the pronunciation of each of the words existing in each language at the universal level. It has several uses such as annotating the pronunciation of words that are not written as they are read, as with French or English, or annotating specific general pronunciations of a particular individual.
Symbols that are used in the IPA are ordered as :
- Consonants (infraglotal and supraglotal, coarticulated)
- Vocals
- Suprasegmental
- Diacritics
There are only symbols for which the sound it represents exists as a phoneme in at least one language worldwide.
Thanks for reading!
-Emmanuel