Can Blue Carbon Help Predict Climate Change Early?
Blue carbon is the carbon captured and stored by coastal and marine ecosystems which act as significant carbon sinks.

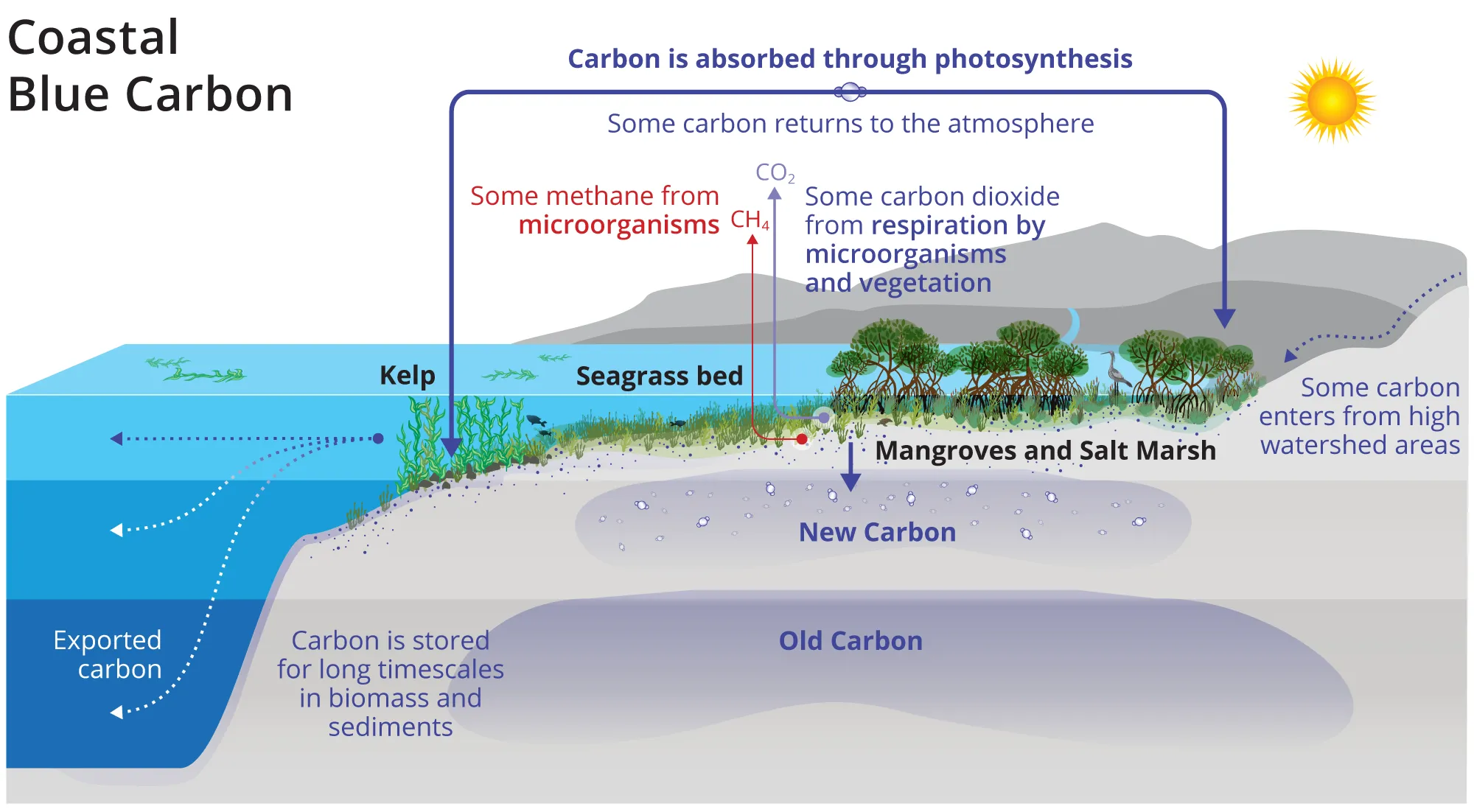
"Blue carbon" is the carbon captured and stored by coastal and marine ecosystems like mangroves, seagrasses, and salt marshes, which act as significant carbon sinks.
Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, helping to prevent its contribution to climate change. It is one of the most effective ways to reduce the concentration of CO2 in the air and mitigate global warming. Carbon sequestration is mainly of two types:
- Land-based carbon sequestration
- Marine carbon sequestration.

Land-based carbon sequestration
- Plants and trees: Forests, grasslands, and other plants act as carbon sinks by absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. Trees and plants store CO2 as organic carbon in their leaves, stems, and roots.
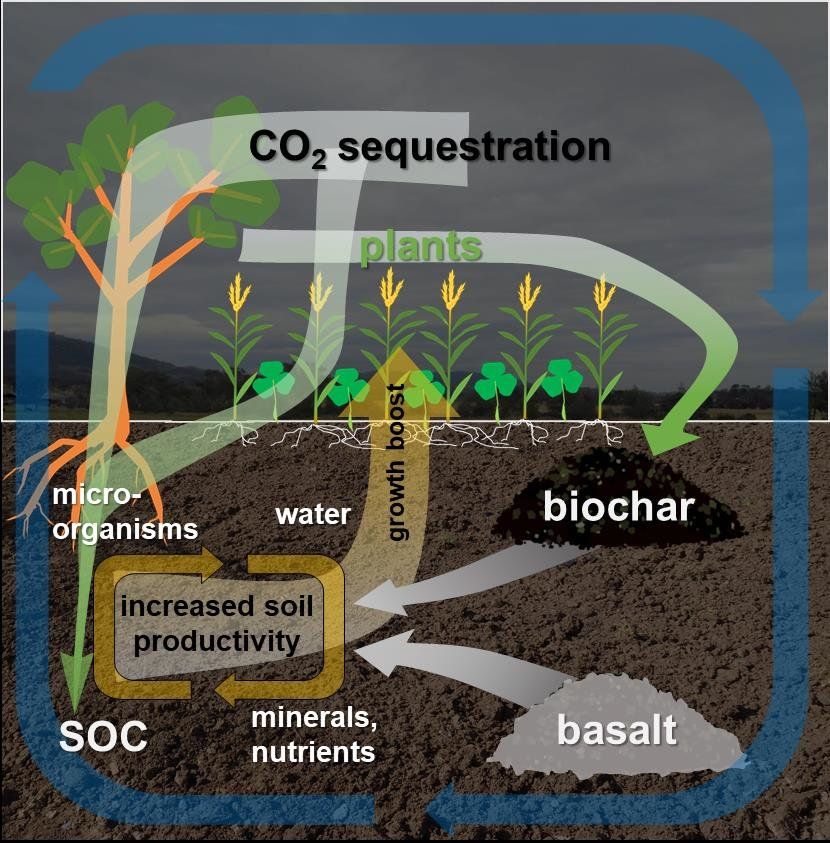
- Soil: Soil serves as a major carbon reservoir. Organic matter, such as dead plant matter and soil organisms, decomposes and stores carbon in the soil for long periods of time.
- Agricultural practices: Sustainable agricultural practices such as no-till farming, agroforestry, and cover cropping can help increase carbon storage in the soil.
- Forests and wetlands: Forests and wetlands (such as peatlands) are important carbon reservoirs. Forests alone store up to 80% of the Earth’s terrestrial carbon.
Benefits of land-based sequestration:
- Restores ecological health.
- Increases biodiversity.
- Improves soil fertility.
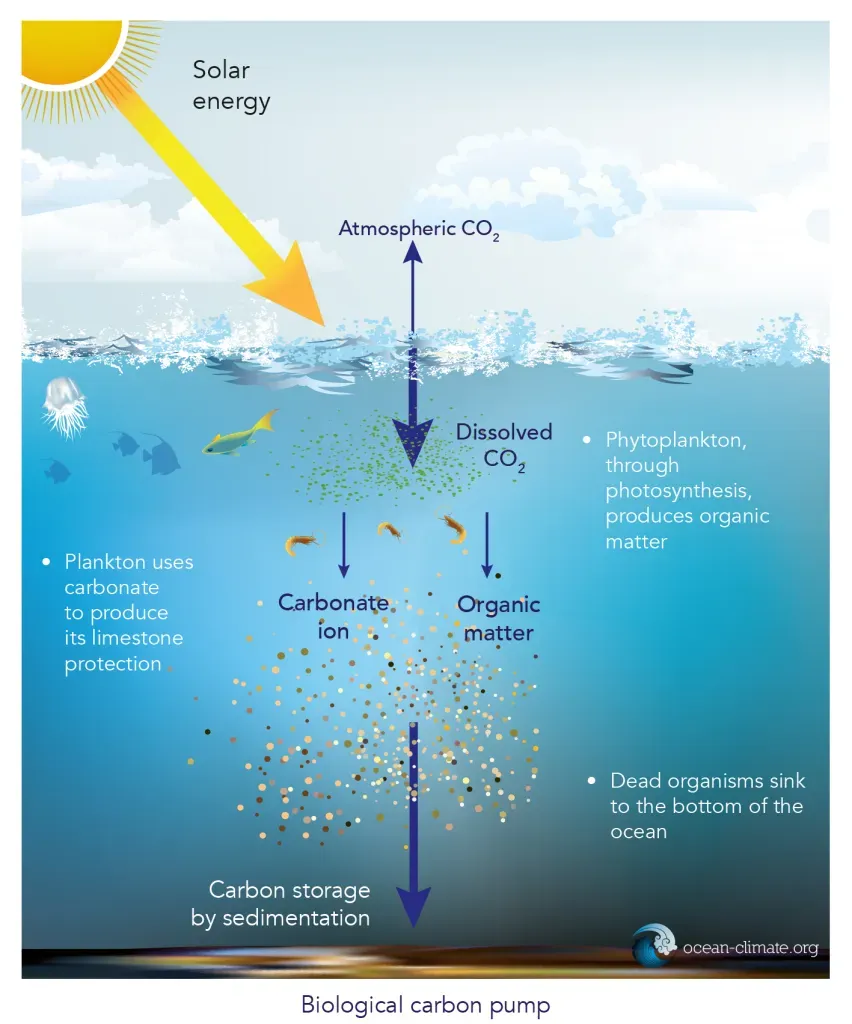
Oceanic (Marine) Carbon Sequestration
- Phytoplankton: The ocean's surface is a key area where carbon is absorbed. Phytoplankton, tiny marine plants, absorb CO2 through photosynthesis and, when they die, their carbon content sinks to the ocean floor, where it can be stored for thousands of years.
- Marine Plants: Seagrasses, mangroves, and salt marshes also sequester carbon. These ecosystems capture carbon through both living biomass (plants) and the sediment beneath them. When the plants die, the carbon in their biomass can be trapped in sediment for long periods.

Benefits of oceanic sequestration
- Protects marine biodiversity.
- Mitigates the effects of ocean acidification.
- Reduces coastal erosion.
Sometimes use Technology for Carbon Sequestration (Artificial)
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): CCS involves capturing CO2 emissions from industrial sources or power plants and storing them underground in geological formations, such as depleted oil and gas fields or deep saline aquifers.
- Direct Air Capture (DAC): This technology directly extracts CO2 from the atmosphere and either stores it underground or uses it for products like fuels or building materials.

Benefits of technological sequestration:
- Reduces emissions from difficult-to-decarbonize industries.
- Can be deployed alongside renewable energy sources.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Change
Carbon sequestration helps to offset emissions by removing CO2 from the atmosphere. It is a critical component of efforts to limit global temperature rise, as outlined in the Paris Agreement. By reducing atmospheric CO2, sequestration can slow the rate of climate change, preserve ecosystems, and prevent extreme weather events caused by a warming planet.
Benefits of Blue Carbon
By storing carbon, blue carbon ecosystems help reduce the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere, thus mitigating the effects of climate change. Coastal ecosystems provide crucial services, such as shoreline protection from storm surges, erosion control, and habitat for marine life. Blue carbon ecosystems support a wide variety of marine and coastal species, including commercially important fish, marine mammals, and endangered species like dugongs and sea turtles.



