The Chemistry of Drinkable Water Treatment
Water needs chemistry because it helps us understand how to keep it clean and how to use it in the way possible. Chemistry is very important for water and for people. Water and chemistry are connected in ways. Water needs chemistry to stay clean and safe. Chemistry helps us take care of water.

Introduction: Why Water Needs Chemistry
Water is really important to us and chemistry is a part of that. Chemistry helps us understand water. We need to know about the chemistry of water to keep it clean and safe for people to drink.
The chemistry of water is what makes it so useful to us. Water is used for lots of things like drinking and washing. It is also used in lots of industries like manufacturing.
So water needs chemistry because it helps us understand how to keep it clean and how to use it in the way possible. Chemistry is very important for water and for people. Water and chemistry are connected in ways. Water needs chemistry to stay clean and safe. Chemistry helps us take care of water.

Water is really good at breaking down things. People call it the " universal solvent" and that makes sense. Water helps things like minerals and nutrients get where they need to go in our bodies. There is a bad side to this. Since water is so good at breaking down things it also picks up stuff like pollutants and heavy metals. It gives bad tiny living things a great place to grow. Water is like an edged sword. It helps us by moving essential things, like electrolytes through our bodies but at the same time water also picks up pollutants.
Water is never really, on its own. Water moves through the ground and rocks and pipes and tanks. It is always touching something. Every time water touches something it picks up a bit of that thing. By the time water gets to a lake or a river it is not just water anymore. Water is a mix of all sorts of things. Water is always. It is really complicated.
Making water to drink is not just about getting rid of the dirt. It is a careful process that involves a lot of chemistry. The people in charge have to make sure they kill the things in the water like pathogens without hurting people who drink it. They also have to get rid of contaminants without taking away the taste of the water or making it unstable. Frank Spellman says in The Science of Water that the way we treat water now is like what nature does. We do it faster and better and we do it for a lot of people. Water treatment is a job and water safety is very important so the people who make water safe to drink have to be very careful with the water.
In the world we live in today this process is always happening without us noticing it. A lot of water goes through treatment facilities every day. If there are small mistakes with the chemicals it can affect a lot of people. The water you drink from a glass is the result of decisions about chemicals and most of these decisions happen without us realizing it. This article is about how chemistry plays a role in making sure the water we drink is safe. It is about how chemistry is between the raw water and the safe water we drink, between the raw water and our safe hydration, between the raw water and the water that is safe for us to drink.
1. Chlorination: The Double-Edged Sword
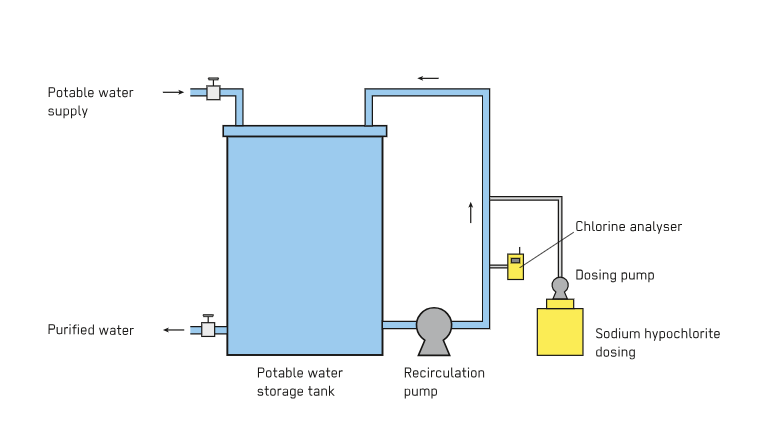
Chlorination has made a difference in public health. This is really clear when you look at what happened before chlorination was introduced in the 1900s. For example in Jersey City in 1908 they started using chlorination. Before that people got really sick from diseases, like cholera and typhoid. These diseases were everywhere. A lot of people died from them.
Michael J. McGuire wrote a book called The Chlorine Revolution. In this book he says that using chlorine in water made a difference. It stopped people from getting sick when they drank contaminated water. Because of this the number of people dying from typhoid went down to zero in just a few years. Chlorination really changed things for health.
Chlorine was really good at what it did. It was not just that Chlorine was good at killing things. Chlorine was also very practical. You could move Chlorine around safely. You could store Chlorine for a time. You could use just the right amount of Chlorine when you needed it. This made Chlorine perfect for cities that were getting bigger. It was also great for water systems that were getting bigger too. Chlorine was good for these things because it was so easy to use.

How Chlorine Works at the Molecular Level
When you add chlorine gas (Cl₂) or hypochlorite (NaOCl) compounds to water they make acid. Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is the thing that really does the job when it comes to chlorination. The reason hypochlorous acid is so good at killing bacteria is that it is small and does not carry any charge so it can easily get through the walls of bacterial cells.
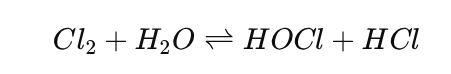
Hypochlorous acid gets inside the cells. Messes up the enzymes and damages the genetic material, which kills the bacteria. Hypochlorous acid is really effective at killing organisms because it can get inside the cells easily.
Chlorine is different from antibiotics. Antibiotics target things in our body. Chlorine works in a very simple way. It just oxidizes things. This means chlorine is really good at killing things. The good thing about chlorine is that bad microorganisms like bacteria do not become resistant to it easily. This is because chlorine does not just target one thing. It targets a lot of things through oxidation. So microorganisms like bacteria have a time becoming resistant to chlorine. Chlorine is very effective because of this.
The thing that really matters but people often forget is pH. When the pH level is low hypochlorous acid is in charge. When the pH level is high it turns into hypochlorite ions. The problem is, hypochlorite ions are not very good at killing germs. So the people who run the water treatment places have to be very careful with the water chemistry and while they are adding chlorine to it. If the pH level changes a little bit it can make a big difference in how well the water gets disinfected. So, pH is really important because it affects how hypochlorous acid works and that is why treatment facilities keep a close eye on the pH level of the water.

People often wonder why chlorine is still used. Chlorine is still used because it is very good at killing things like bacteria and viruses. Chlorine is still used in places, like swimming pools and water treatment plants to keep the water clean and safe for people to use. The reason chlorine is still used is that it is cheap and it works well. Chlorine is still used to clean drinking water and make it safe for people to drink. Many cities and towns still use chlorine to clean their water because it is a way to keep people from getting sick. Chlorine is still used in lots of ways and it is still a very important tool for keeping people healthy.
Chlorine is really good at sticking around. When chlorine is added to water, a little bit of it stays active as the water moves through the pipes. This means the water is protected from getting contaminated for a time even after it has left the treatment plant. This protection is especially important in pipes where leaks happen a lot and the water pressure keeps changing. Chlorine is very good at keeping the water safe in these systems.
Chlorine is a choice because it does not cost a lot of money and it can be used in big systems. This makes chlorine very important, for cities that have to provide water to a lot of people like millions of people. Chlorine is used in these municipal systems because it is cheap and it works well for a large number of people.
The Downsides
Chlorine has some points. When chlorine mixes with the stuff that is in water it can make some other things that are not good for us like trihalomethanes(THMs) and haloacetic acids(HAAs). The government keeps an eye on these things because chlorine can make these compounds and they might be bad for our health if we are around them for a long time. Chlorine and these compounds are a deal because chlorine is used to clean the water we drink.
To deal with this problem modern treatment plants use a lot of steps. They take out the material before they add chlorine and they are very careful with how much chlorine they use. This way utilities can reduce the things that are made when they clean the water and they can still keep the water safe. Modern treatment plants do this to make sure the water is clean and safe to drink.
A Common Misunderstanding
A strong smell of chlorine does not always mean that the water has much chlorine in it. Sometimes the smell is because of chloramines. These are things that form when chlorine mixes with ammonia (NH3) or other bad things in the water. It is funny that this smell usually means that the water does not have chlorine, not that it has too much chlorine.
2. Ozonation: Powerful but Short-Lived
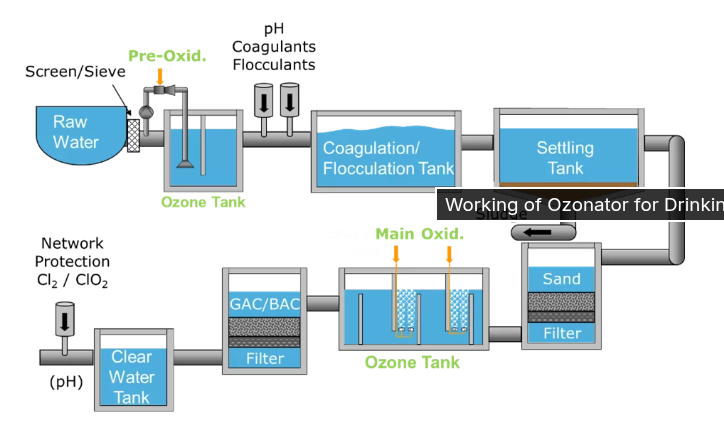
Ozone is a choice for water systems where the taste and odor of the water are really important. A lot of companies that bottle water and big city water treatment plants like the ones in Paris and Los Angeles use ozone to make the water clean. Ozone is the thing they use to kill the bad stuff in the water.
People are starting to think about water treatment in a way. Nowadays people want their water to be safe to drink and also taste good. Ozone is really good at making water taste good. Ozone is what people are looking for when they want their water to be nice to drink.
The Chemistry Behind Ozone
Ozone is made right at the site by sending oxygen through electrical fields, which is like what happens when there is a lightning storm. When ozone is mixed with water it cleans the water in two ways. First the ozone attacks the layer of tiny living things like germs. Then the ozone breaks down into particles called hydroxyl radicals(•OH). These particles are very good at breaking down things in the water like old medicines and pesticides. Ozone is really good at cleaning the water because it can get rid of these things. The ozone breaks down into hydroxyl radicals(•OH) and these radicals are what actually destroy the pollutants, like pharmaceuticals and pesticides in the water.
These radicals are strong chemicals that are used to clean water. They are able to break down things that chlorine's not strong enough to break down. The radicals are very good at getting rid of stuff in the water.

Strengths and Weaknesses
Ozone is really good at killing things like Giardia and Cryptosporidium that other things, like chlorine cannot kill. Ozone does not leave a taste or smell in the water because it breaks down into oxygen very quickly. This means the water will just taste like water with oxygen in it which is what we want. Ozone breaks down into oxygen.
Ozone does not keep the water safe for a time after it leaves the treatment plant. When ozone is used to clean water that has bromide in it it can also make bromate. Bromate is a thing because it can cause cancer. That is why ozone is often used with a bit of chlorine. The chlorine helps keep the water safe as it moves through the pipes to peoples homes. Ozone and chlorine work together to make sure the water is safe to drink.
3. Water Softening: Chemistry for Convenience
Hard water is not bad for you to drink. But, it causes problems every day. The calcium and magnesium in water, which it gets from moving through limestone and soil with lots of minerals, makes a kind of scum build up in pipes and things like dishwashers. This scum also makes soap and laundry detergent not work well as they should. Hard water is really the problem because it has all these extra minerals, like calcium and magnesium that make all these troubles.
This scaling is a problem that gets worse over time. It makes homes and industries use energy and cost more money to maintain. The energy efficiency of homes and industries goes down because of this scaling. Maintenance costs for homes and industries also go up.

Ion Exchange in Practice
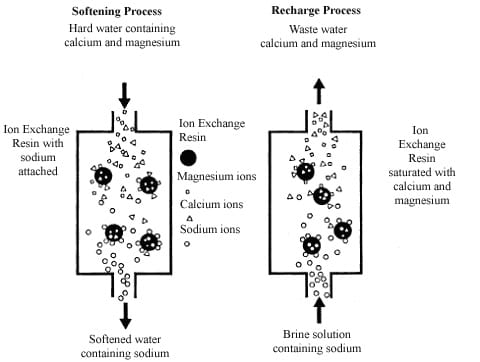
Water softeners use tiny balls called ion-exchange resins. These tiny balls have a charge and they have sodium in them to start with. When water that is hard flows through the water softeners the calcium and magnesium in the hard water stick to the balls really strongly. This makes the sodium go into the water. The calcium and magnesium stick to the water softeners because they like the balls more than the sodium does. Water softeners work because of this. The tiny balls in the water softeners are what make the water soft.
This exchange does not need any electricity or complicated machines. It only needs a connection between chemicals. The chemical affinity is really all that is required for this exchange to happen. The exchange is based on chemical affinity.
The Role of Salt
Salt is used for one thing: to help the resin work. It does not make the drinking water taste better. Every and then a strong salt solution is used to clean the system. This salt solution pushes out the calcium and magnesium that have built up. The salt can be used again to make the resin work properly. The resin is what needs to be fixed and salt is what helps to fix it.
Softer water has sodium in it. This is something to think about. People with some health problems should drink water that has not been treated. This is what doctors often tell them to do. Softened water is not good for everyone, with certain medical conditions so they should stick to untreated water.
4. Reverse Osmosis and Desalination
In some places people do not have a lot of water. So they have to use desalination to get water. Desalination is really important in these places. The common way to do desalination is by using reverse osmosis. Reverse osmosis is used all over the world now.
These systems are really cool because they use chemistry in a big way. They bring together membrane science and thermodynamics and fluid mechanics to make things work on a scale. This is what makes these systems so interesting. They use chemistry and membrane science and thermodynamics and fluid mechanics all at the same time to get the job done at an industrial scale.
How Reverse Osmosis Works
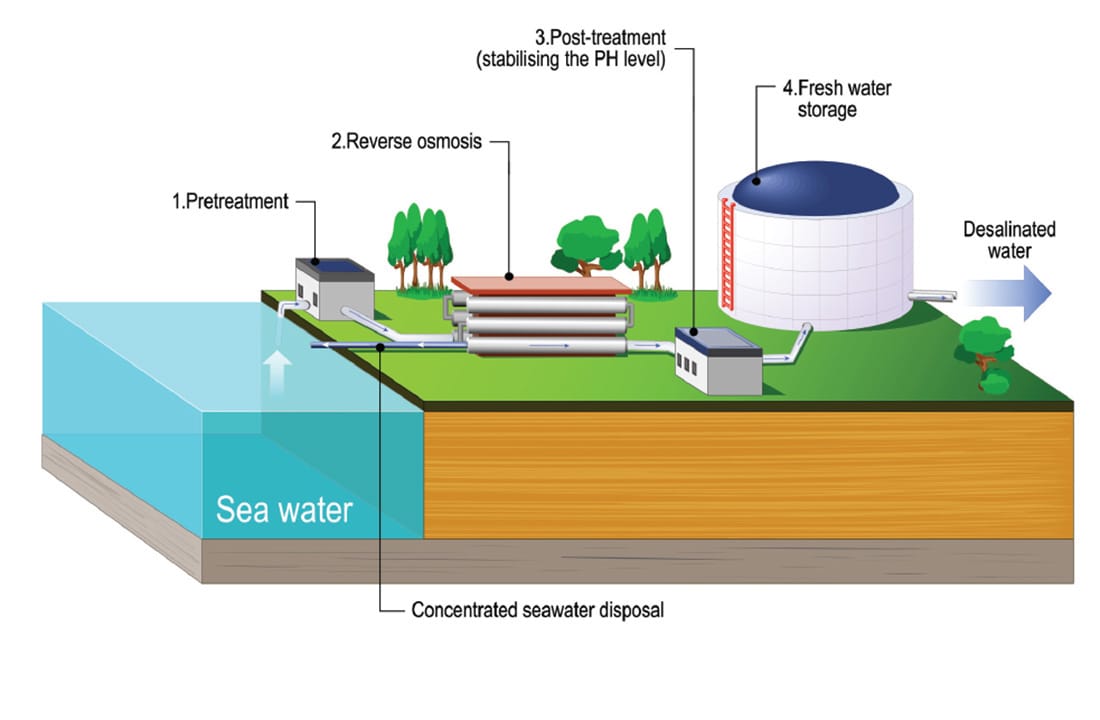
Water normally goes from places where it's not very salty, to places where it is very salty. Reverse osmosis is different. It uses a lot of pressure to push the water the way. This makes the water go through a membrane that has tiny holes in it. The water has to go through this membrane. Reverse osmosis makes the water move from areas of solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration, which is the opposite of what water normally does.
The membrane lets water molecules go through. It stops salts, microbes, heavy metals and other bad things from getting in. What you get is really water. The membrane makes sure that water molecules can pass through. This gives you exceptionally pure water.
Why Remineralization Is Necessary
So you have this pure water, like RO water and it does not have all the good minerals in it. This kind of water can actually be bad for things because it is corrosive.
To make it better people often do something to the water. They pass the treated water over things like calcium carbonate. This helps to get the minerals in the water and it makes the water taste a lot better. The water needs these minerals to be stable like a balance of minerals. It is not bad for things. This is why people add minerals back to the RO water.
Case Study: Water Management in Oman
Traditional Solutions
For a long time Oman used the Falaj system. The Falaj system is a way of moving water from one place to another using gravity. It is like a channel that brings groundwater from one place to another even if it is far away. The Falaj system does not need any machines or special chemicals to work. It just needs people to plan it carefully and work together as a community. The Oman people used the Falaj system for the Falaj system to work.
Modern Challenges
The population is growing fast. We do not have water from natural sources. Today Oman gets 85 percent of its drinking water from special plants that remove salt from seawater. These plants are called reverse osmosis desalination plants. Oman relies heavily on these reverse osmosis desalination plants, for its drinking water.
Preserving Tradition
Oman is still doing something old even with all the new technology around. They have something called Sabils which are like public fountains where people can get free drinking water. The Sabils are really cool because they show how old ideas and new ways of doing things can work together. The old ideas and the new chemical engineering are mixed together in a way in the Sabils. Oman has a lot of Sabils. They are very important to the people of Oman because they are a part of their cultural tradition of Sabils.
Conclusion
Clean drinking water does not just happen. People make sure it is safe to drink on purpose. Clean drinking water is the result of chemical control. Chlorine helps keep drinking water clean for a long time. Ozone is very good at killing things in clean drinking water. Reverse osmosis helps people get drinking water even when clean drinking water is hard to find. Each of these methods for making drinking water is a balance between keeping people safe, having the right equipment not costing too much money and what people think clean drinking water should be, like.
The next time you turn on a tap, remember that what flows out is not just water, it is chemistry working quietly, constantly, and successfully in the background.
References
Al-Barwani, H. H., & Prathapar, S. A. (2021). Desalination in Oman: Past, Present and Future. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 11(1), 1-15.
American Water Works Association (AWWA). (2011). Water quality & treatment: A handbook on drinking water (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional.
Black & Veatch Corporation. (2010). White’s handbook of chlorination and alternative disinfectants (5th ed.). Wiley.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2024). Water Disinfection with Chlorine and Chloramine. Retrieved from cdc.gov.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (2023). Basic Information about Disinfection Byproducts in Drinking Water. Retrieved from epa.gov.
Gleick, P. H. (2000). The world's water 2000-2001: The biennial report on freshwater resources. Island Press.
Langlais, B., Reckhow, D. A., & Brink, D. R. (Eds.). (1991). Ozone in water treatment: Application and engineering. CRC Press.
McGuire, M. J. (2013). The chlorine revolution: Water disinfection and the saving of lives. American Water Works Association.
Spellman, F. R. (2007). The science of water: Concepts and applications (2nd ed.). CRC Press.
World Health Organization (WHO). (2022). Guidelines for drinking-water quality: Fourth edition incorporating the first and second addenda. WHO Press.






