During World War II, there were events and battles that turned the balance of power between the nations of the world, drew new borders and killed millions, but where did the story begin?
Initially
Hitler's occupation of Austria in March 1938, Czechoslovakia the following year and Poland in September 1939, then Italy's threat to invade Albania, was a direct reason for Britain and France to declare war on the Axis powers.
War erupted in Europe and the German army was ahead of all European fronts, occupying most of the countries and entering Paris, but its attack on the Soviet Union in June 1941 made him leave his back exposed to the British.
The United States did not enter the war at first, but imposed a petroleum embargo on Japan and banned the export of iron to it. On December 7, 1941, Japan attacked the American fleet in the Pacific Ocean at Pearl Harbor in Hawaii, so the United States entered the war against the Axis powers.
In the 1820's, the United States adopted what was known as the "Monroe Doctrine" or the principle of neutrality, a declaration made by US President James Monroe in 1823, stating that European countries should not extend their colonial influence to America, and the United States' commitment on its part not to interfering with European problems or relations.
The most important battles and station
The war witnessed many battles that formed basic stations in it, and had its impact on its course and results, as is the case in the battles of Stalingrad, Meadow, Alamein, landing the Normandy, and dropping the two atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The Battle of Stalingrad

is considered one of the most important major battles in the Second World War, and took place in Stalingrad - the city that was later known as "Volgograd" - during the German military campaign against the Soviet Union, which lasted about six months between August 1942 and February 1943 .
Germany attacked the city with the Air Force and then entered it after turning it into ruins. The fighting inside it intensified fiercely with the Red Army, and the Germans managed to subjugate most of the city's areas, but they failed to break the last defensive lines of the Red Army in the West Bank of the Volga.
In November 1942, the Red Army launched two simultaneous attacks and managed to besiege and encircle some 250,000 German forces, and with the Germans unable to supply their soldiers, their forces collapsed and Commander Frederick Paulus surrendered on February 2, 1943, along with most of the Sixth Army.
The casualties in the battle amounted to about one million people, which made it one of the bloodiest battles in the history of wars.
The Battle of Midway

The battle of midway took place in June 1942, six months later the Japanese attack on the American fleet in "Pearl Harbor", during which the US Navy managed to repel the attack by the Japanese Imperial Navy on the island of "Midway", and damage the Japanese fleet.
Military historian John Keegan called it "the most brilliant and decisive blow in the history of naval wars."
The Battle of El Alamein
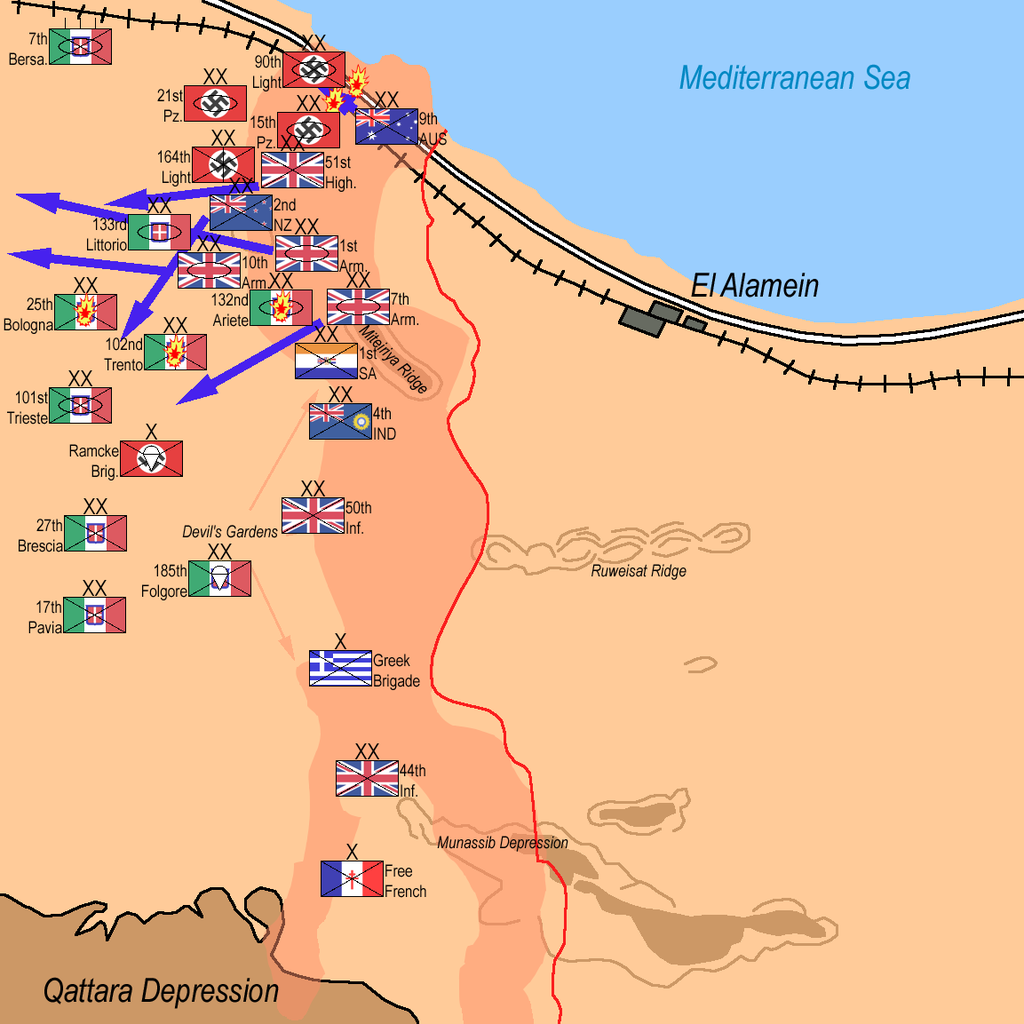
It took place in November 1942 on Egyptian soil between German and Italian forces led by Irvine Rommel, and British forces led by Bernard Montgomery.
And it was one of the most important tank battles throughout history. After the victory of the German forces in the desert battles, the British forces were able to defeat the Axis forces in this battle and expel them, and the most famous German commander Rommel was defeated, and the Axis countries began to loom on the horizon.
Normandy landing

On June 6, 1944, the Allied forces, led by American General Dwight Eisenhower, landed a military landing in northern France on the Normandy shore. More than two hundred thousand soldiers, most of them Americans, were sent from Britain, Canada, and France.
The operation is considered the largest military landing in the twentieth century, and it enabled the liberation of the region from the German army, and the losses on both sides amounted to three thousand dead, and six thousand wounded, captured and missing.
After the German defeats in this battle, the Allies entered Germany in December 1944, and Italian revolutionaries executed "Mussolini" and suspended him from his feet in a lighting pole in Milan. Hitler committed suicide on April 30, 1945, and Germany surrendered.
The atomic bomb and the end of the war
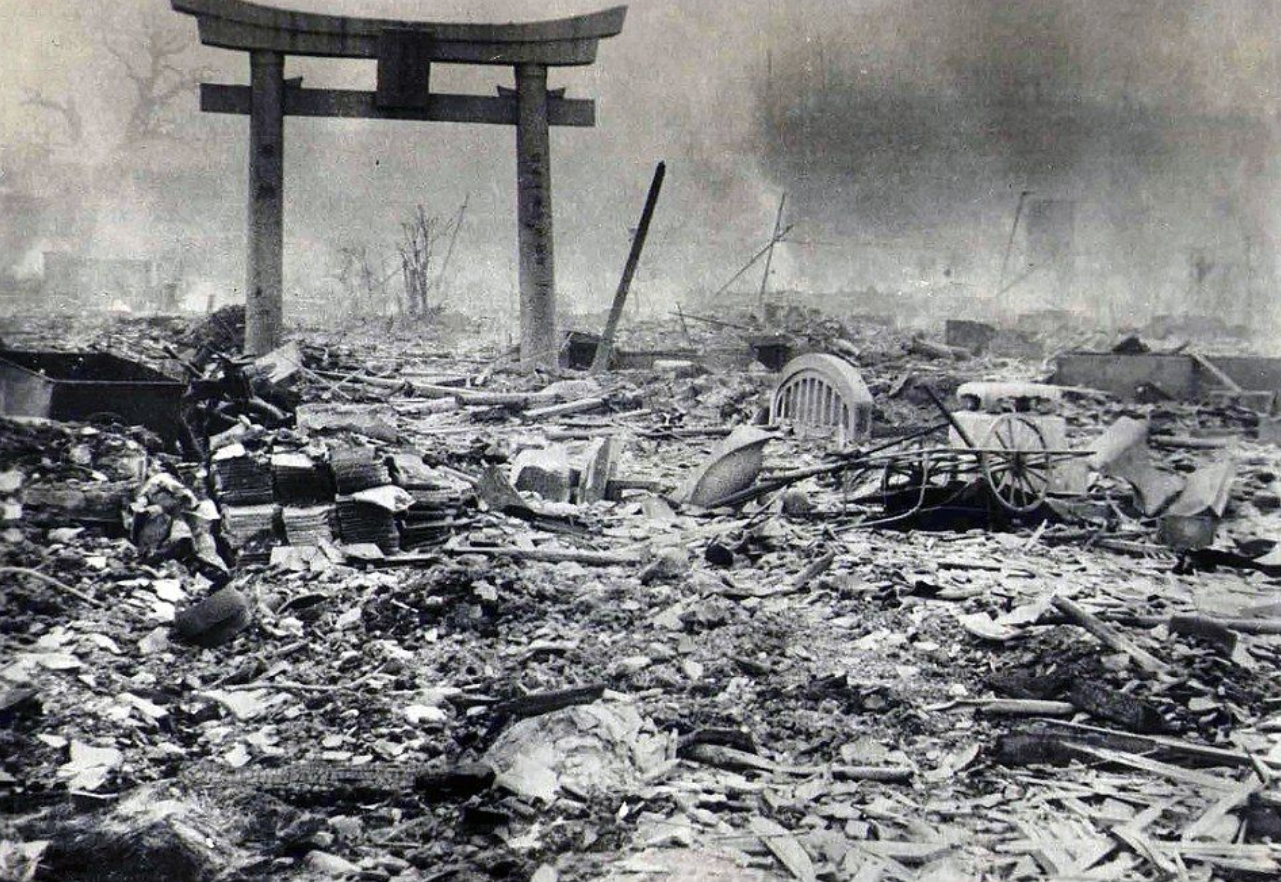

Despite the surrender of Germany, the Japanese continued to resist, and the war did not stop forever until after the bombing of the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki with two atomic bombs that formed the first use of atomic bombs in history.
The first "little boy" was thrown into Hiroshima on August 6, 1945, and a uranium bomb weighing more than 4.5 tons, missed the target a little and fell 800 feet away from it.
One minute after it was dropped, 66,000 people lost their lives and 69,000 were injured.
The second "fat man" was thrown into Nagasaki on August 9, 1945, and a plutonium bomb was dropped in the center of Nagasaki. In one moment, 39,000 people were killed and 25,000 residents were injured.
Subsequently, Japan signed the surrender document unconditionally on September 2, 1945, and three days later, the US flag was raised over Tokyo.
Human losses and political consequences
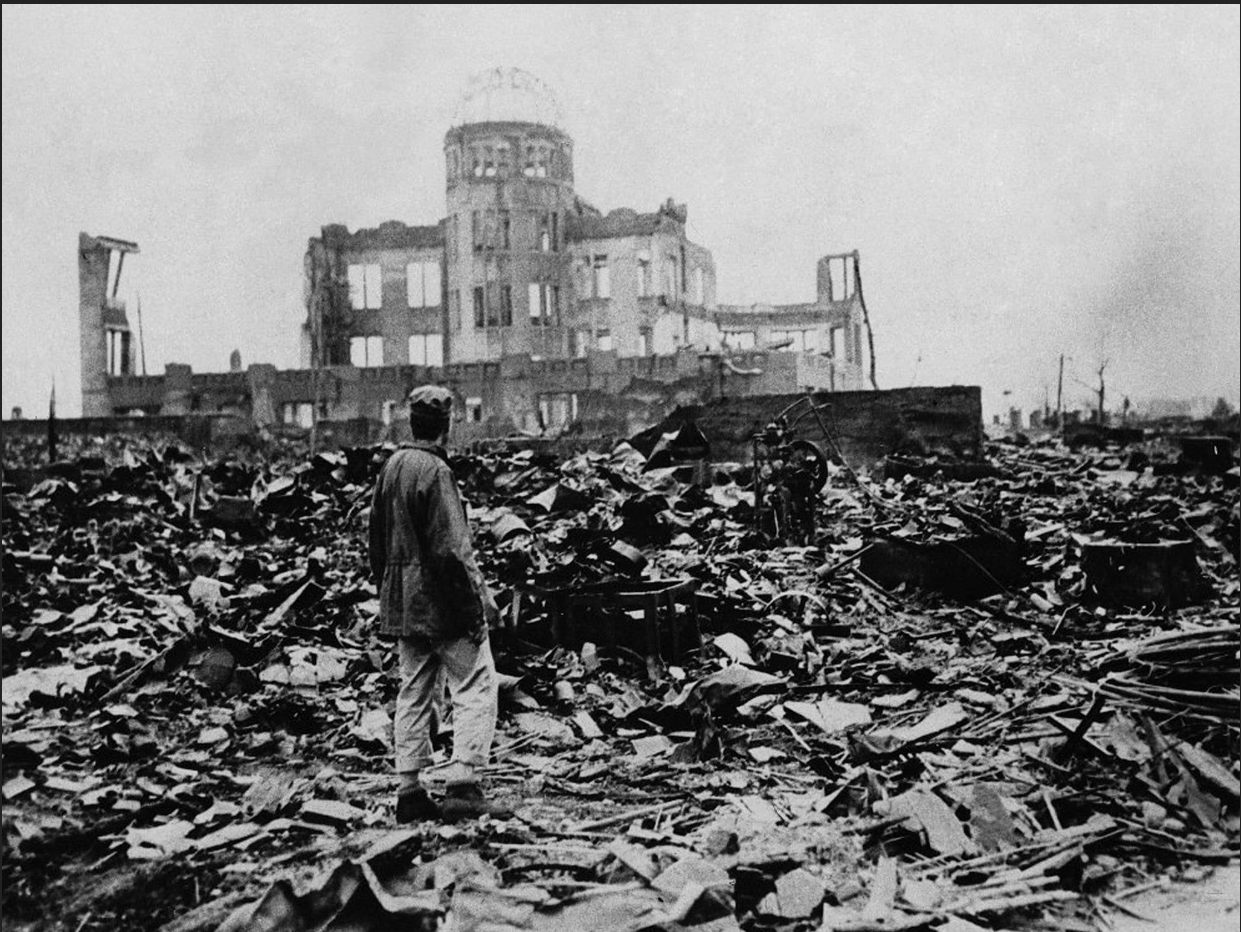

The Second World War ended after six years of fierce fighting, in which humanity lost about 17 million soldiers and twice that of civilians.
One of its results was the victory of the Allied countries over the Axis powers, but the US's use of the atomic bomb in the war to compel Japan to surrender opened the door of the frantic race to possess weapons of mass destruction.
On the political level, one of its most prominent results was the formation of the map of the new international powers after the war, the emergence of the United States of America as a major actor in the new international order, and the establishment of the United Nations to dedicate the new map.
Through the United Nations, America has tried to confront the rising European powers whose influence extends overseas (Britain and France in particular) and the Soviet Union, which has been expanding its influence.
Through the international organization, America will have - according to this perspective - a mechanism to compete with these two giants, which must be contained within the framework of the international community.
To diminish the European role, the United States encouraged the right to self-determination of the colonies, and the Marshall Plan - which it developed to rebuild a devastated Europe - contributed to keeping these countries indebted to the United States, as well as its contribution to US influence in shaping political systems and direct war effects in Europe.
Consider subscribing us to get updated news right into your email. Thanks


