Beirut Explosion and Ammonium Nitrate: What Caused the Devastating Explosion
Even though ammonium nitrate itself is pretty much stable, it acts as a strong oxidizing agent. In simple words, it acts as a good source of oxygen.
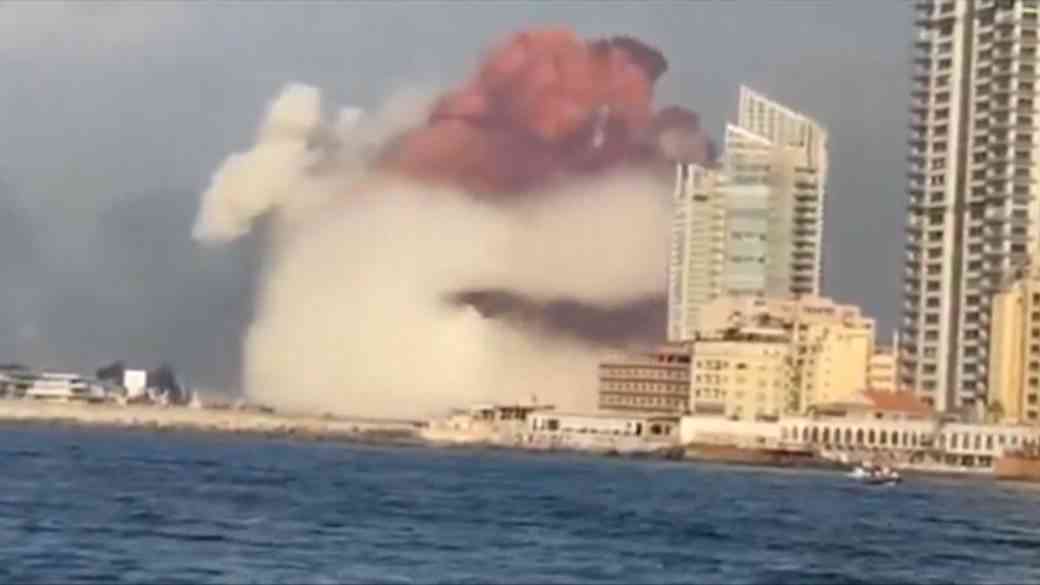

At around 6:08 pm local time on 4th August, Beirut, the capital city of Lebanon, trembled as a massive explosion caused citywide destruction. The death toll exceeded 135, and more than 5000 were injured according to Aljazeera.
According to the Lebanese government, 2750 tons of ammonium nitrate was the driving force behind this massive explosion, which was stored in a warehouse for a very long time. (Article continues below)
Today, we will discuss the science behind the explosion.
What is ammonium nitrate?
Ammonium nitrate is a crystalline water-soluble chemical. The chemical formula of ammonium nitrate is NH4NO3. It is widely used in the agriculture industry as a high nitrogen fertilizer. When decomposed, it produces nitrogen which is necessary for plant growth.
Consider supporting me by donating here
Besides being used as a fertilizer, ammonium nitrate is also widely used as an explosive in combination with other materials that promote explosion.
The science behind the explosion
Even though ammonium nitrate itself (NH4NO3) is pretty much stable, it acts as a strong oxidizing agent. In simple words, it acts as a good source of oxygen. Ammonium nitrate must be exposed to heat or fire to cause an accelerated decomposition which can cause fire and result in an explosion.
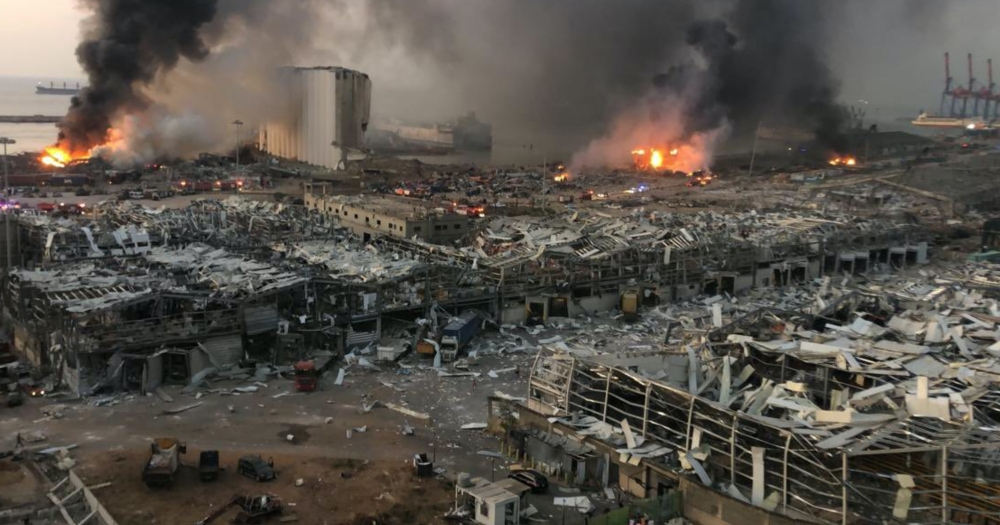

From fire/heat, ammonium nitrate takes energy, which unstabilizes the material and in turn, produces more heat. If ammonium nitrate is stored in an open space, the heat can dissipate in the environment easily which reduces the chance of a possible explosion. However, if it is stored in a warehouse or a container, it is hard for the resulting heat to escape; this facilitates explosion.
The rapid decomposition of the chemical fertilizer (yes, ammonium nitrate is widely used as a fertilizer) creates gaseous compounds like water vapor and nitrous oxide. This creates enormous gaseous pressure within a tiny area. Due to the ongoing decomposition, the pressure keeps increasing and causes the gas to expand at a very high speed. This is what we call “explosion” or “detonation.” This whole process takes very little time, and enormous energy is released which creates a shockwave.
Several videos circulating in social media suggests that the Beirut explosion was probably set out by fire. The dark-orange-ish mushroom cloud which erupted right after the explosion, indicates the production of nitrous oxide which is the result of ammonium nitrate decomposition.
Second tweet I've found now of the entire explosion. Appears to have been taken by some fast moving craft about 1 KM from shore. pic.twitter.com/6V8tI9WLpC
— The Intel Crab (@IntelCrab) August 4, 2020
The explosion was so massive that the sound was heard from as far as Cyprus, according to a report published by the BBC. This indicates just how much energy was released all of a sudden from the explosion of 2750 tonnes of Ammonium Nitrate.
Join us on Hive.blog and earn rewards for your contribution by clicking here
Recommended reading:



