Main Translation Modes Explained
Everything you need to know about Translation Modes! #theroad_to_be_a_translator

SO, on part 1 we learned about the definition of Translation, we learned about the history about Translation, we found out who the "Father of translation" is, and we also learned about how translation is important to our lives.
In this part we will learn about a very important information in the translation industry: Modes of Translation in detail.

Modes of Translation Industry.
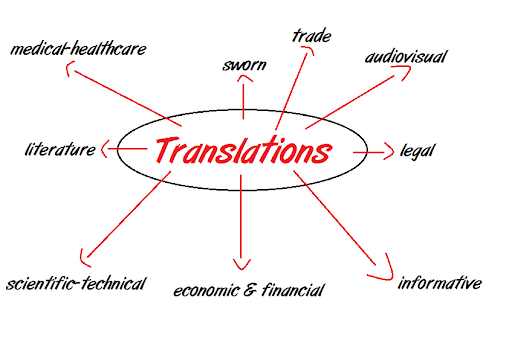
1-Literary translation: literary translation is performed with great difficulty from other types of translation. We find that the translator is required to transfer meanings from one language to another, as well as describing the emotional state and feelings experienced by the original author, and consequently moved to the citizens of the country of the original author, which made him rise, excel and appear In his home country by becoming widely known, and from this point of view the translator should be careful; Through its skill and experience.Literary translation is of huge importance. It helps to shape our understanding of the world around us in many ways.
What makes Literary Translation So difficult?
The translation of literature is highly different from other translation types. the huge size of texts concerned in literary translation sets it apart. the mission of a translation which runs through thousands of words is not a mission for anyone to take it, neither is the re-making and creating of poetry in a very new language while not losing the sweetness and essence of the first work.

One of the biggest challenges of literary translation is the translator need to balance between the source and target language feelings and convey them right
and to make the target language get constant feelings and responses just like the original. this will be notably difficult once it involves translating poetry.
Poems are scripts written with unbelievable attention to detail and messages. Not solely area unit the words and phrases vital, It’s a difficult task to complete simply in one language, as well as once making an attempt to recreate a poet’s work throughout a translation. Daniel Otto Hahn, director of nation center for Literary Translation, sums up the difficulty beautifully: “There’s not a single word in any of the languages I translate that can map perfectly onto a word in English. So it’s always interpretative, approximate, creative. Anything that is, itself, a ‘linguistic’ quality will by definition be anchored in a particular language — whether it’s idiom, ambiguity, or assonance. All languages are different.”
Religious translation: Religious translation is a type of translation of great importance. It is an important means of spreading a specific religion throughout the world, as well as getting to know the rules and laws related to that religion for its affiliates in other regions. For example, there are great needs for religious translation related to the noble "hadiths" and Islamic jurisprudence for Muslims in non-Arabic speaking countries, such as China , India, Japan, Africa, etc.

Scientific translation: It is one of the important types of translation, and scientific translation requires elements that differ from other translations. Due to the need to be familiar with scientific terms, and to try to find alternatives to them in the target language, especially in light of the emergence of new from those terms every period.

Requirements of Scientific translator
According to London Institute of Linguistics, to be a scientific translator one ought to have:
- broad information of the subject-matter of the text to be translated;
- a well-developed imagination that allows the translator to envision the instrumentality or method being described;
- intelligence, to be ready to fill within the missing links within the original text;
- a way of discrimination, to be ready to select the foremost appropriate equivalent term from the literature of the sector or from dictionaries;
- the power to use one’s owns language with clarity, terseness, and precision; and
- sensible expertise in translating from connected fields. In short, to be a technical translator one should be a somebody, or engineer, a linguist, and an author
Economic translation: Currently, commercial transactions are spread between countries and each other, either directly, or through multinational companies, or through international stock exchanges, etc., so economic translation appeared and spread; In order to achieve balance in the light of common interests between businessmen in different countries

The areas of financial and economic translation vary, as they include several tracks, the most important of which are: Translating financial documents in accordance with established commercial regulations. Financial documents include all types of reports, data and revenues. Budgets of all kinds. Commercial releases. Commercial contracts. Mailing. Financial records of individuals or companies. Investment documents. Feasibility study of projects. Business and business plans. Tax documents. Commercial ads. Websites and emails related to business and economics. Economic research. Profit and loss reports. and Trade offers.
Legal translation: Legal translation is among the important types of translation, which has become a great place in the corridors of societies in different countries, and the need for it increases day after day; Due to the interaction and communication between different tongues, it is therefore necessary to know the laws, contracts and clauses that promote rights among citizens of countries.Legal translation may also imply that it is a specific type of translation only used in law, which is not always the case.

(As law is a culture-dependent subject field, legal translation is not necessarily linguistically transparent. Lack of transparency in translation can be avoided somewhat by use of Latin legal terminology, where possible. Lack of transparency can lead to expensive misunderstandings in terms of a contract, for example, resulting in avoidable lawsuits. Legal translation is thus usually done by specialized law translators. Conflicts over the legal impact of a translation can be avoided by indicating that the text is "authentic" i.e. legally operative on its own terms or instead is merely a "convenience translation", which itself is not legally operative. Courts only apply authentic texts and do not rely on "convenience" translations in adjudicating rights and duties of litigants.) info from (Wikipedia)
Media translation: Media translation is one of the types of translation required by the requirements of the times, in light of the spread of dozens of media outlets, whether traditional which is represented in newspapers and magazines, or electronic, which is represented in the Internet and the sites and applications that exist in it, as well as satellite channels that are not limited to It is in the current period, and the news is transmitted very quickly between the various countries, so interest in media translation has increased at the present time.

Multimedia translation can be applied to various fields, including cinema, television, theater, advertisement, audiovisual and mobile device communication
Interpretation: What is interpretation?
The basic definition of interpretation, consistent with the Webster wordbook is that the “action of explaining the which means of one thing; the manner something is explained or understood.”
In terms of language, the definition of interpretation ought to be broader: rendering a spoken or signed message into another spoken or signed language, protective the register and which means of the language content.
It is the spoken or signed language communication between users of various languages. A language interpreter or linguistic communication interpreter should not solely quickly and punctiliously interpret which means, however conjointly tone and intent of the initial message into the target or understood language.
There are literally 3 primary modes of interpreting:
Simultaneous, Consecutive and sight translation.
Simultaneous interpreting: The interpreter listens and renders the message within the target language at constant time because the speaker is speaking.
Consecutive interpreting: The interpreter speaks when the language speaker has stopped speaking.
Sight translation: AN oral rendition of a written language.
How is interpretation performed?
Often we expect of a language being understood face-to-face, like during a court, college or medical facility. However, remote decoding may be performed through telecommunication decoding or video remote decoding.
No matter the format, the interpreter should have glorious language proficiency, be able to quickly analyze and transfer messages between languages and cling to skilled ethics and standards of observe.

SO, this was a large run through into nearly everything you need to know about translation mods and what about them. I really hope you benefited and enjoyed.
Saif A. Asaad Aljuboory.

