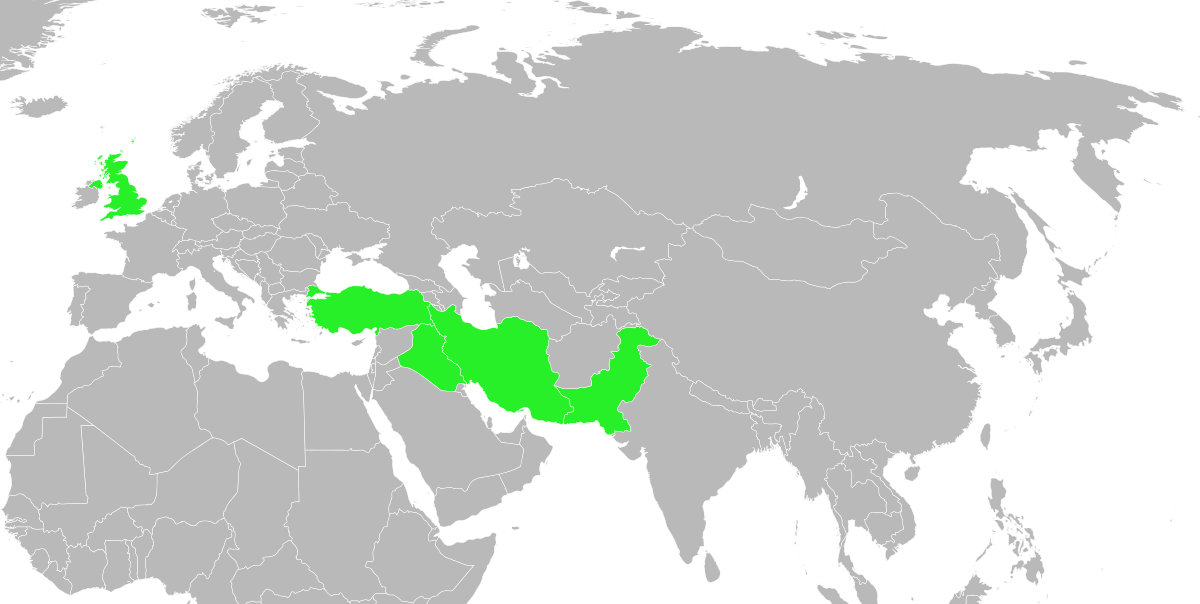
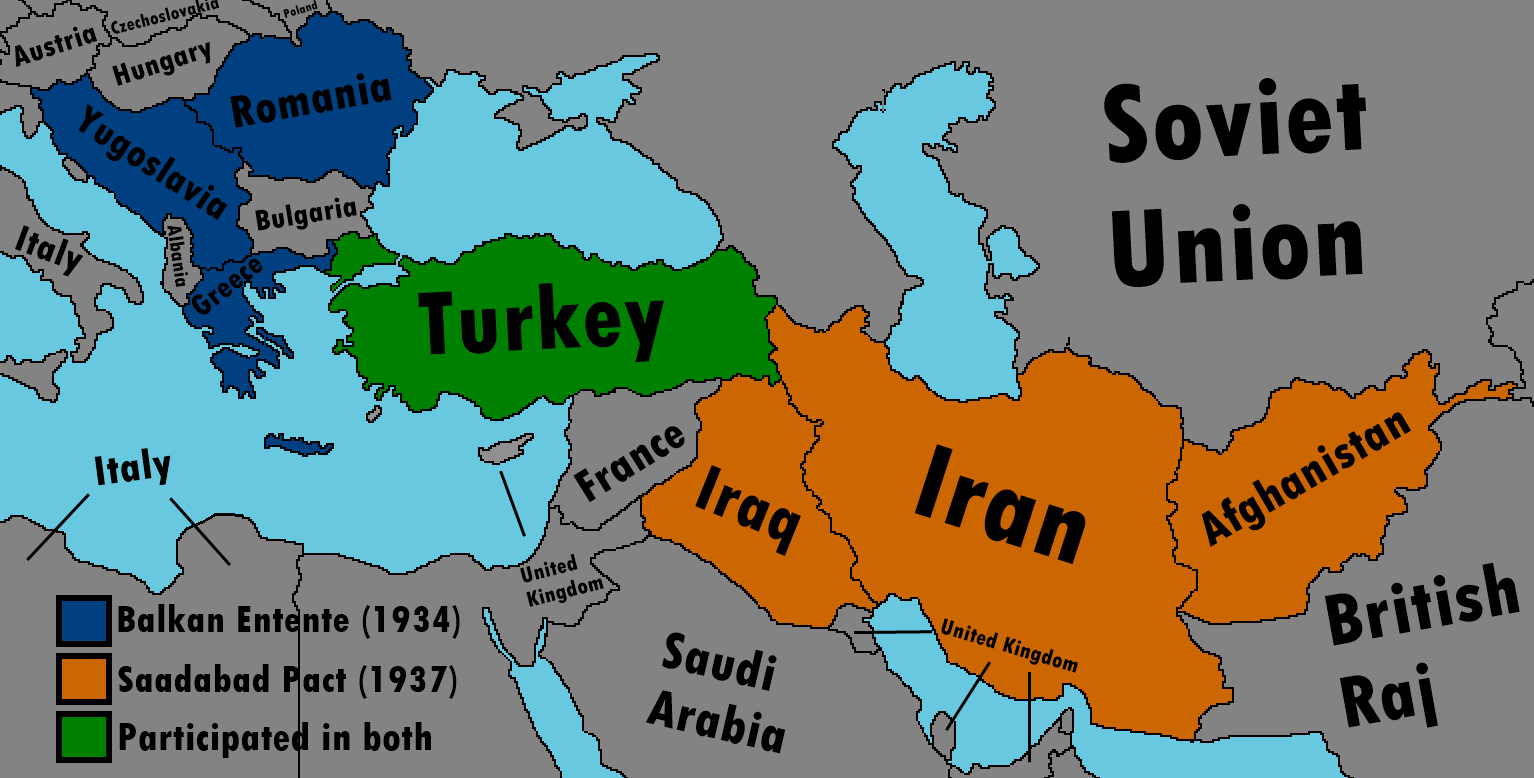
SaadAbad Agreement : It means "Middle East Concord"; It was a non-aggression treaty signed by Turkey, Iran, Iraq and Afghanistan on July 8, 1937. The charter lasted five years. The charter was signed at the Saadabad Palace in Tehran and was part of an initiative of the Greater Middle East Relations led by King Muhammad Zahir Shah of Afghanistan. Ratifications were exchanged in Tehran on June 25, 1938 and entered into force on the same day. It was registered (deposited) in the League of Nations treaty series on July 19, 1938.

The charter was planned by the United Kingdom. British diplomacy sought to strengthen its influence in the Near and Middle East, and to use this new grouping in its anti-Soviet policies, (((as well as against growing German and Italian interest in the region))). In addition, three of the four signatories to the Charter were involved in joint efforts to combat Kurdish separatism in Iraq, Iran, and Turkey. The Kurds in those countries had tried to create an independent state in the name of the Republic of Ararat 1927-1931.

In Iraq, the left-leaning military government led by Bakr Sidqi (1936-1937) was less Arab nationalism than other Iraqi governments. Sedky was a Kurd and his Prime Minister, Hikmat Suleiman, was Turkmen. Therefore, they were inclined to strengthen ties with non-Arab neighbors. Turkey has sought friendship with its neighbors while licking the wounds of its defeat in World War I.
Preparing, signing, and ratifying the charter :-
Initial negotiations on the Saadabad Charter began in 1935 due to the complexity of the political situation, due to the Italian aggression against Ethiopia. On October 2, 1935, the foreign ministers of Iran, Turkey, and Iraq met in Geneva,Switzerland prior to the League of Nations Council session, drafted and signed the text of the Charter.
In November 1935, Afghanistan joined the proposed charter. However, it took about two years between signing the initials and the final signature on the charter, as the participants believed that the effectiveness of the charter should be complete before the final signature, by resolving the border disputes between the participating countries before the final signing of the charter. Those issues were pending between Iran and Afghanistan, Iran and Turkey, and the most severe were between Iran and Iraq. The differences between Iran and Afghanistan were settled in the same year by Turkish mediation. The thorny issues between Iran and Turkey require that a special Turkish mission travel to Tehran in April - May 1937 be resolved.
Finally, on the day before the signing of the charter, July 7, 1937, the ongoing dispute between Iran and Iraq over the demarcation of the borders in the (Shatt al-Arab River), and a final agreement on that issue was signed on July 4, 1937 in Tehran. Meanwhile, the foreign ministers of the four countries met in the Iranian capital, where they signed the Saadabad Charter, thus creating "Middle East Entente." The exchange of Ratifications took place in Tehran on June 25, 1938, and the Charter entered into force on the same day, and was deposited in the Register of the League of Nations on July 19, 1938.
Charter implications :-
Iran obtained its intention to amend the borders of the Shatt al-Arab, because the sovereignty of Iraq was complete over the Shatt al-Arab before this treaty, and therefore all ships passing to the Abadan port were under Iraqi sovereignty. Iran said in its negotiations before Saadabad that the borders in the Shatt al-Arab are a violation of its national sovereignty on the basis that unusual circumstances accompanied the demarcation process between England and Iran, in a period of political and military turmoil and pressure it suffered from Turkey in 1913 and 1914.
The important thing here is that Iran unambiguously linked its agreement to join the League of Nations with Iraq by removing the injustice that had befallen it by signing the "Astana Protocol 1913", which was the protocol that set the boundary line between Ottoman Turkey, which at the time had full sovereignty over the Shatt al-Arab (Iraq and its heir). Legal in the three Districts (Basra, Baghdad, Mosul) and the shah Of Iran. The Astana Protocol 1913 was based on the Second Erzurum Agreement of 1847, which guaranteed complete freedom for the passage of Iranian ships, but with the supremacy of the Ottoman High State over the entire Shatt al-Arab.
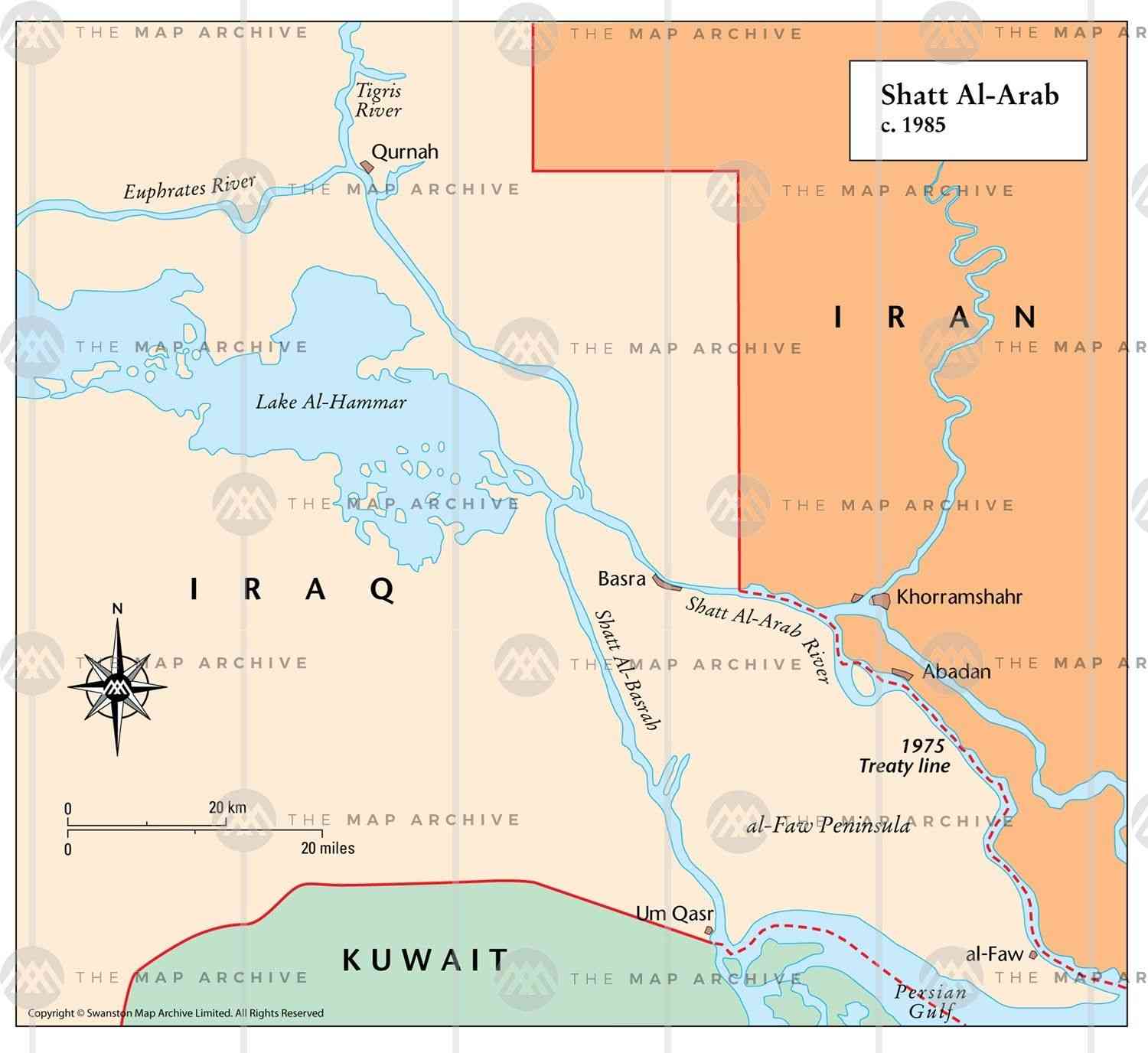
The "Saadabad" agreement served, from a material and political perspective, the interests of the Iranian government and the countries of Turkey, Afghanistan and Iraq, because the Ararat Mountains of important strategic status went to the sovereignty of Turkey. And with the demarcation of the boundary line between Iran and Iraq on the basis of the ownership of Reza Shah for the sources of oil in western Iran with sovereignty over half of the Shatt al-Arab (Arvand River) on the basis of international principles the bottom or third line , which gave Iraq sovereignty over the oil tankers arriving to and from Abadan Port, which had to pay sums to Iran and Iraq, which is under English protection.
After signing the "Saadabad Agreement" and in a speech delivered to the Iranian parliament at the opening of its eleventh session, Reza Shah said: "The Saadabad Agreement is unprecedented in the East at this turbulent time in world history, and it is a great help to sustain world peace."
Iran had what it wanted in the end, then Tehran returned and modified the joint borders with Iraq in the Shatt al-Arab again (note the expression and the position rolled from complete sovereignty of Iraq to 50% to the rolling of the border line towards Iran and ended with Iranian supremacy in the Shatt al-Arab!) Again to " The famous 1975 Algiers agreement, which gave Iran much more than its share before the Saadabad Treaty, not to mention the Astana Protocol or the second Erzurum agreement of 1847.
Cluster organizational structure and additional treaties :-
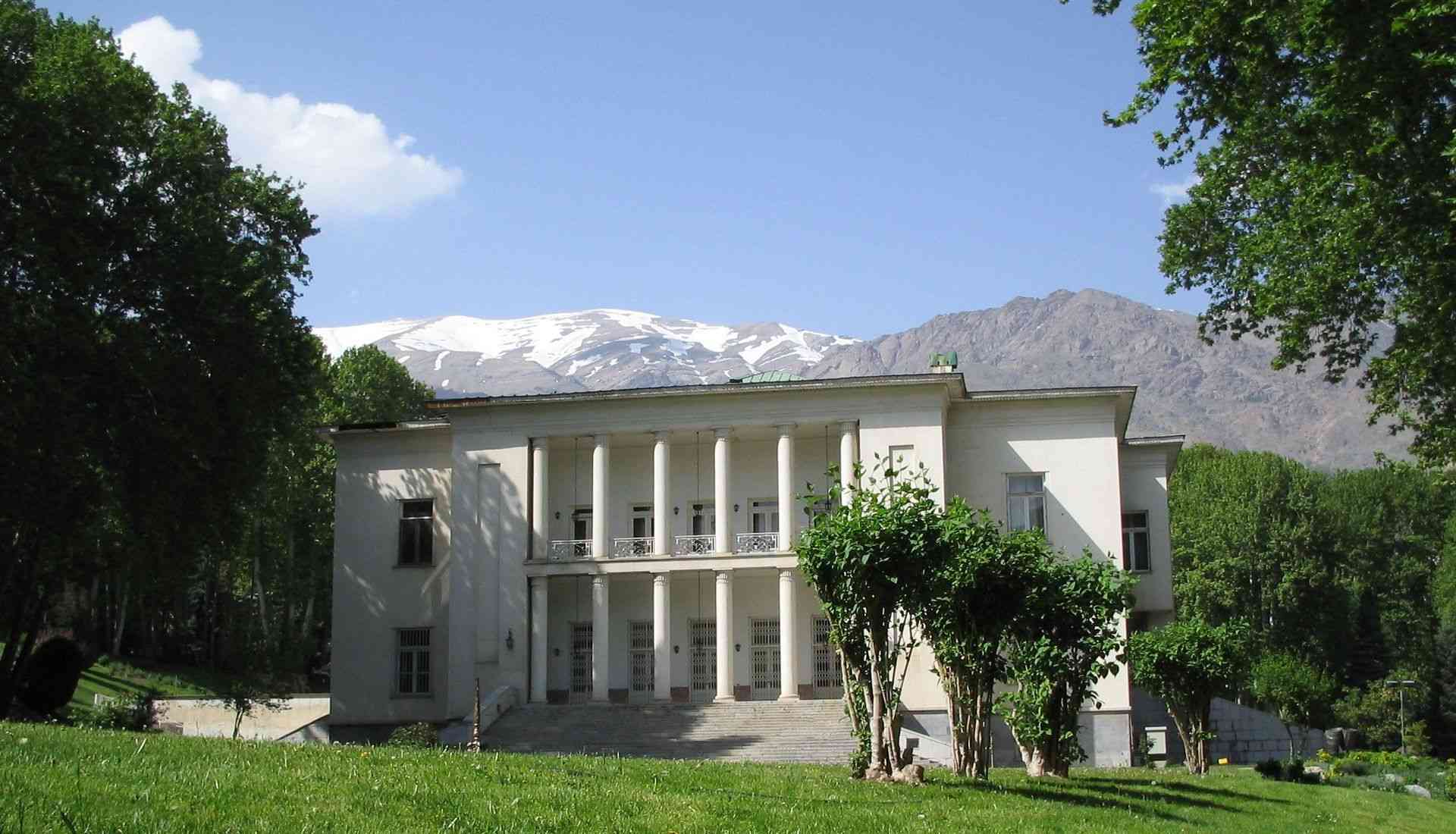
Saadabad Palace, Tehran, where the charter was signed.At the same time as signing the charter and establishing the "Permanent Council for Conciliation, the Middle East" - consisting of the four Middle Eastern countries represented by their foreign ministers (along the lines of the Balkan Accord and the Baltic Accord), it was supposed to convene at least once a year. The first meeting of the Al-Wefaq Council in the Middle East was held immediately after the signing of the charter, in which a number of decisions were taken on joint action in the League of Nations.
This was followed by a series of Iranian-Iraqi agreements: on July 18, 1937 the two countries signed a friendship treaty, and on July 24, 1937, a treaty for the peaceful settlement of common differences; In 1938, they decided to establish a commission to demarcate the borders. And in December 1939 an agreement for border inspectors.
Middle East ES activities In 1938, Turkey, thanks to its participation in the Middle East Accord, was able in part to achieve the takeover of the Sanjak of Iskenderun ( Hatay,Turkey ) from the French Mandate of Syria, claiming that the majority of its population is Turkmen. It established the independent state of Hatay on its soil, then in 1939 it conducted a referendum that included the brigade to Turkey. However, the next branch of Al-Wefaq (such as the Balkans Accord and the Baltic Accord) did not address the foreign policy as a united front, as the foreign policies of the member states seemed to vary their interests and preferences, which made the creation of the Saadabad Alliance as a Middle East agreement ineffective in international public relations. In Qasr Al-Omar, there are similar efforts to settle the border disputes between Iran and Iraq to normalize relations between the two countries.

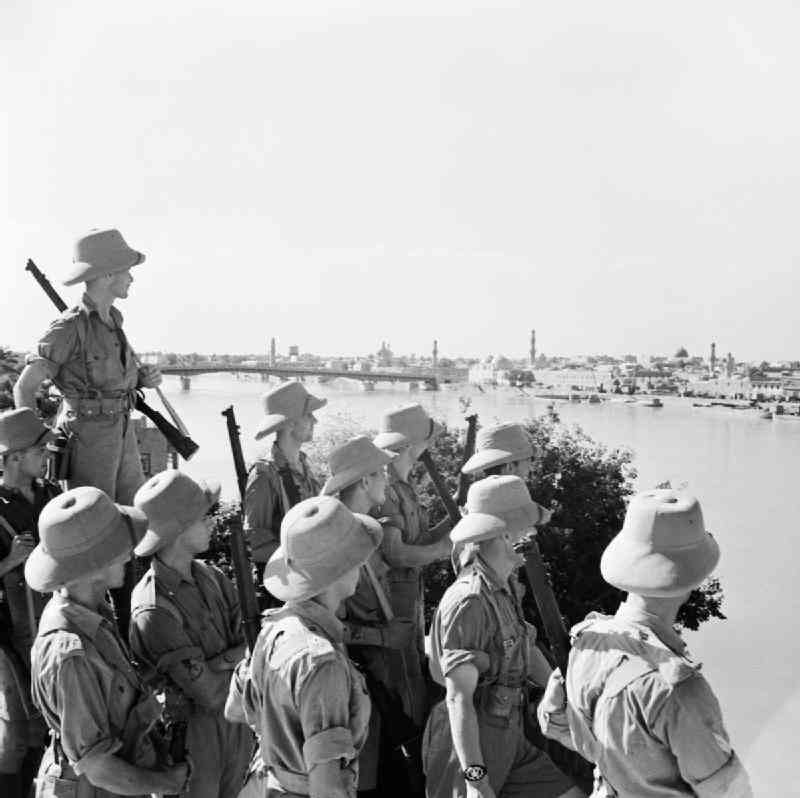
During World War II (1939-1945), members of the Middle East Accord took inconsistent attitudes toward warring alliances. Germany planned to control the oil-rich Near and Middle East, satisfied, albeit temporarily, with the presence of Syria and Lebanon under the command of the French Vichy regime of the Third Reich, and the Germans encouraged Arab nationalist movements in areas under British control such as Palestine and Iraq, The Germans also tried to drag their influence into Turkey and Iran. Italy has also made a number of attempts to subjugate Arab countries to establish a sphere of influence in North Yemen, and to carry out a series of unsuccessful military raids on British bases in southern Arabia (in particular the aerial bombardment of the colony of Aden).
However, in 1941, the allies managed to liberate Syria and Lebanon, followed by a pro-German military coup in Iraq that led to the thirty-day Anglo-Iraqi War and the defeat of Iraq in it. The actions of the Soviet Union and diplomacy forced Turkey to abandon its plans to enter the war against the Soviet Union in Germany side. As a point in the chain of events in the region, the Soviet English occupation came to Iran, subjecting Iran to preventing it from falling into the fascist bloc.


The collapse of the Middle East ES :-
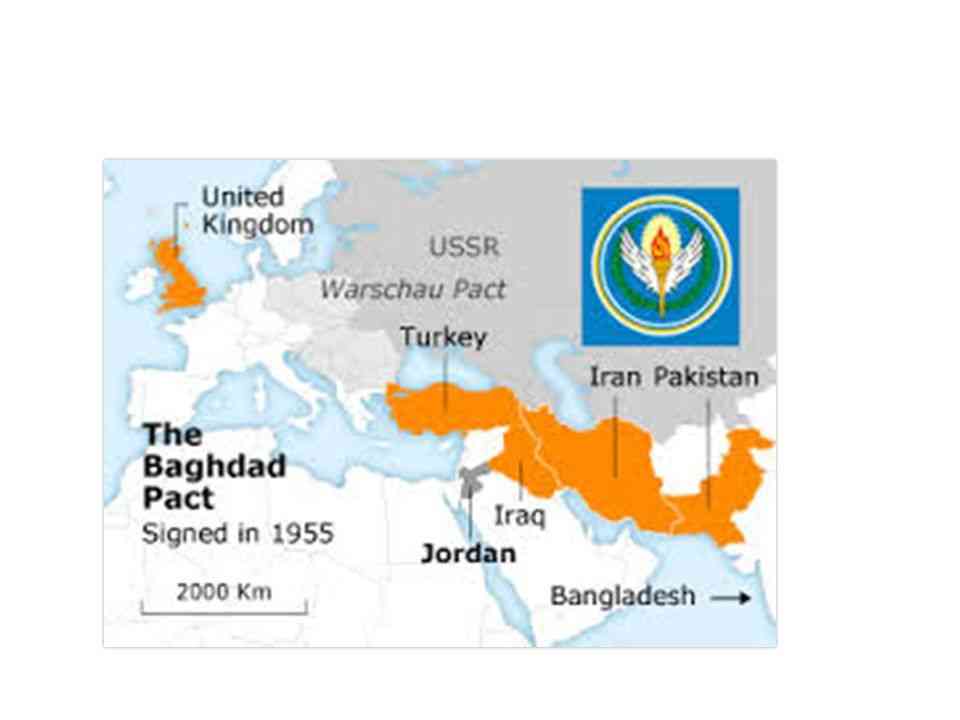
Everything that happened in the region confirmed that the Middle East accord had collapsed, and that the Saadabad Charter no longer exists. Officially, however, in 1943 the charter was automatically renewed for another five-year period, as no signatory objected to it. Consequently, the Middle East accord continued on paper until 1948. After the war, English-American diplomacy began efforts to revive the Saadabad Treaty, hoping to use it to draw up a plan to create an eastern bloc (which includes alongside Iraq, other Arab countries), and directed against the Soviet Union. This was partly done with the signing of the Baghdad Alliance in 1955, which created the NATO-allied CENTO bloc, but without the participation of Afghanistan.