UNDERSTANDING DRAGON: A Sneak Peek In The Mindset Of Communist China Part 1
A deep dive in the psyche of Communist China. This study details the events of last century in China, the transformation from dynastic polity to Asia's first republic and then the transition into a single party communist state.
Prologue
Chinese civilization is among the oldest in the world, the roots can be traced back to nearly 4000 years, to the fertile basins of Yellow River in the plains of northern China. These first settlers of Yellow river started spreading out absorbing aboriginal tribes, in east, north & south; by the time of Confucius (500 B.C.) these men and women of the basins of Yellow River had occupied most of the country between today’s Great Wall of China and the Yangtze River.
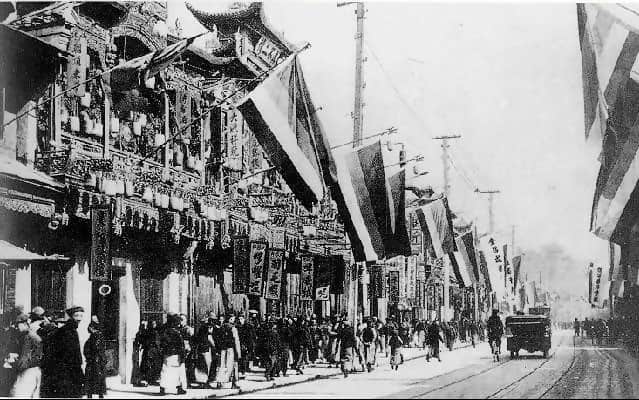
For thousands of years numerous warlords, monarchs and various dynasties ruled this mystic land, so many of them rose and fell, until the Xinhai Revolution of 1911. Comprising of various revolts and uprisings, a struggle that went on for over a decade, this people’s revolution finally overthrew the last emperor, Pu Yi, a six year old, on 12th Feb 1912 and hence came the end of Qing Dynasty and the Republic of China (ROC) was established.
First ever people’s government led by Sun Yat-sen took charge of the country, Asia’s very first republic was born & the pride of Han Chinese was restored. However, the road wasn’t easy ahead, as they say, winning the land is easy part, tough part is, running the land; a gargantuan task of bringing the five major ethnic groups - Hans, Manchus, Mongols, Huis, and Tibetans, under one fold and take them forward in the new world awaited.

To make things worse, radical western ideologies like Marxism and anarchism were gaining traction among the Chinese intellectuals and eventually a Left-Wing was formed within KMT, always at edge with the Right Wing of the party, struggling for the control & power. Eventually, "Communist Party of China" or "Chinese Communist Party" was formed in the July of 1921.
With the death of KMT leader Sun Yat-sen in March of 1925, a new chapter was about to start, he was succeeded by, Chiang Kai-shek a Right Winger, who initiated countless actions to diminish the position of the Left Wing (Communists). Chiang Kai-shek had tasted success in his northern expedition to neutralize warlords, riding on that euphoria he turned on to the communists and marched on Shanghai massacring nearly 5000 communists in that city alone. Over the next two years another 20000 communists were killed by the nationalists.
It was August of 1927, when the CCP officially raised ‘The Red Army’ with Mao Zedong as it’s Commander-in-Chief, this was the Nanchang uprising that started another chapter of bloodiness, massacres, killings, abductions, following a gory civil war that lasted almost 2 decades.
By the time WW2 ended with Japan’s defeat in pacific in 1945, Chiang Kai-shek led republicans had lost control over most the mainland China, finally pulling out of the Mainland and shifting Republic of China to the island of Taiwan in 1949.
The Mainland China was now People’s Republic of China (PRC) of “Mao Zedong”. A new era is about to begin..

To understand today’s China & why she does what she does, we need to go back in time and understand, the modern history of the land, its people and the politics associated.
Here is our three part article on the last 100 years of Republic of China and the formation of the People’s Republic of China, or the “Communist China”, “Red China”.
Part 1: Great Leap Forward
Part 2: Relationships & Conflicts with the World
Part 3: Ambitions or Arrogance
Source & References:
1) Cambridge Illustrated History of China. Patricia Buckley Ebrey.
2) The Dynasties of China. Bamber Gascoigne.
3) China Condensed: 5000 Years of History and Culture. Ong Siew Chey.
4) What's behind the China-Taiwan divide? BBC.
5) The Story of China. PBS.