Fiber Optics: How does it work?
Fiber optics have changed the world in many ways than you can imagine. It has changed the way we communicate.

Fiber optics have changed the world in many ways than you can imagine. It has changed the way we communicate. It’s really fascinating that the ability to transmit data through pulses of light. It has opened the door for many world changing innovations in medicine, manufacturing, communications etc. The discovery of fiber optics started with the technology to transmit voice signals over an optical beam.

Firstly, this concept came out in the 1840s, physicists Daniel Collodon and Jacques Babinet showed that the light could be directed along jets of water for fountain displays. Then 30 years later, Alexander Graham Bell developed this awesome technology. By transmitting voice signals, the world started using telephone connection which previously wasn’t possible. Later on, it worked for the faster internet, surgery and dentistry, electronic devices in cars etc. So, today we will know:
- What is fiber optics?
- How does fiber optics work?
What is fiber optics?
ANS:
Fiber optics is the medium or the technology which is associated with the transmission of data using light pulses along a pure glass or plastic strand. It is mainly used for long-distance and high performance data networking. The main principle that works for the fiber optical cable is “Total Internal Reflection”. So, if you look closely at a single optical fiber, you will see these main following parts:
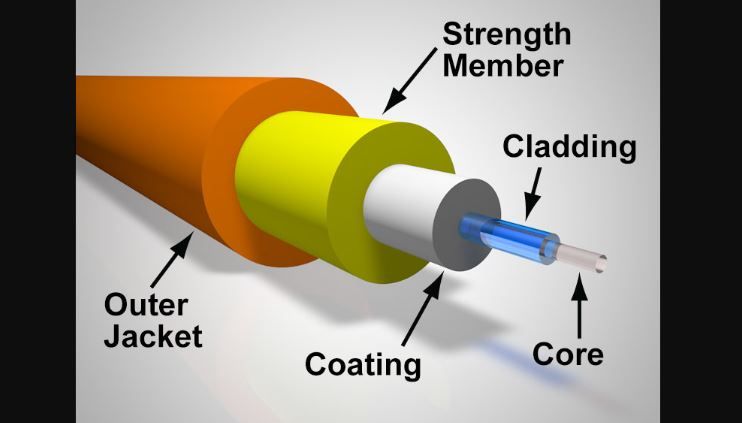
- Core- A thin glass center of the fiber where the light travels through.
- Cladding- Outer optical material surrounding the core which reflects the light back into the core.
- Buffer Coating- It mainly works for protecting the fiber from damaging.
And all these three parts, there is a cable’s outer covering called “JACKET”. Well, let's look at the types of optical fibers. Optical fibers are two types:
Single mode fibers - Small cores (about 9 microns in diameter) which transmits infrared laser light ( wavelength = 1300 to 1550 nm).
Multi mode fibers - Larger cores (about 62.5 microns in diameter) which transmits infrared laser light ( wavelength = 850 to 1300 nm).
How does fiber optics work?
ANS:
The fiber optics works on the principle of “total internal reflection” by light particles or protons that transmits data through it’s cable. The two main parts of fiber optics are known as Code and Cladding which have a different refractive index. "In optics, the refractive index or index of refraction of a material is a dimensionless number that describes how fast light travels through the material." And each refractive index bends incoming light at a certain angle.
There would be a problem as the light rays travel in straight lines, so we must need straight long wire without any bends at all. This could also break the thin glass. But, it’s not quite possible. Instead of this, the optical cables are designed such that they bend all the light rays. Light rays travel continuously in a series of zig-zag bounces off the optical fiber walls when any light signals are sent through this. Though, these light signals do not travel at the speed of light because of the denser glass layers. There are also optical receivers and receptors that receive the transmitted light pulse, decode them to be fit to use and regenerate the optical signals. In a brief discussion, this is how it does work.
In the next article about fiber optics, we will teach you how to splice (combine two cables).
Subscribe to our newsletter to stay updated. THANKS :)

