DNA: The Language of Life
DNA is the central molecule which is responsible for the proper function of all living organisms.

DNA is the miracle molecule of life. Most of the higher-level organisms, such as humans, animals, plants, have DNA as their genetic information carrier. DNA contains all the traits of an organism. DNA is like a recipe book that contains all the information to create RNA and proteins of an organism. DNA can be both double-stranded (dsDNA) and single-stranded (ssDNA). While dsDNA is the most abundant type of DNA in nature, some viruses contain ssDNA as their genome. ssDNA is very rare in nature; thus, we will only discuss dsDNA for convenience.
DNA consists of two complementary strands that form a double helix structure which looks like a twisted ladder. Each strand of the helix is made up of nucleotide monomers. Thus, we call DNA a polymer of nucleotides. When a nucleoside is paired with a phosphate group, it is called a nucleotide. A nucleoside is made up of deoxyribose, a pentose sugar lacking an oxygen molecule in its second carbon and a nitrogen base. DNA contains four types of nitrogen bases which are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). Adenine and guanine are known as purine bases and cytosine and thymine are called pyrimidine bases. The deoxyribose and pentose sugar form the backbone while the sequence of the nitrogen bases forms the instructions carried by the DNA molecule. A phosphodiester bond connects each of the pentose sugar within a strand. The bond between the pentose sugar and the nitrogen base is called a glycosidic bond. The two strands are connected with hydrogen bonds formed between two nitrogen bases of the complementary strands. Adenine pairs with thymine with two hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs with cytosine with three hydrogen bonds.
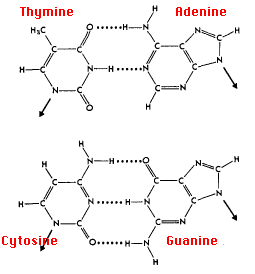
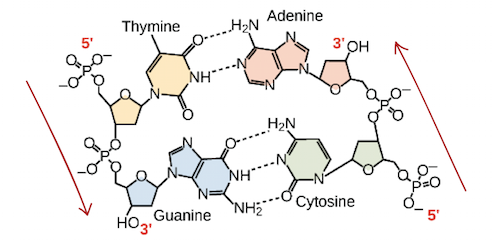
This base pairing is often referred to as Watson-Crick base pairs. So basically, the two strands are held together by the bonds formed between purine and pyrimidine bases. Thus the total number of purine bases and the total number of pyrimidine bases are the same in a DNA molecule. This is known as Chargaff’s rule. The two strands of the DNA double helix run in opposite directions, it is like two humans sleeping in an anti-parallel direction. 5’ and 3’ is used to explain this configuration. These numbers are used to indicate the number of carbon in the pentose sugar backbone. The 5th carbon of a pentose sugar has a phosphate group attached to it and the 3rd carbon a hydroxyl (-OH) group. This gives a DNA strand a direction.
Double helix DNA can be found in three forms known as A form, B form and Z form. The pattern of the nucleotide bases is what forms the genetic code. Human DNA contains around 6 billion bases making it a long molecule. Human DNA is about 3 meters long, so long that without proper packaging, the DNA molecule may be rendered useless as it will be prone to damage. Proper packaging of DNA is necessary for gene expression, replication and to make it more resistant to damage. In cells, DNA is stored as a supercoiled structure. It is done with the help of a specific nucleoprotein called histones.
First, the DNA molecule coils around the histones. This DNA-histone association is called nucleosome. The diameter of the nucleosome is 11 nanometers; thus, it is also known as 11 nm fiber. The 11 nm fiber coils around itself again which results in the formation of 30 nm fiber. Depending on the presence of divalent ions such as Mg2+ this 30 nm fiber can coil in two ways. One is in zigzag form another is in helical. Either way, further coiling of the molecule results in the formation of 300 nm fiber which again coils around itself forming 700 nm fiber. The 700 nm fiber coils around itself again forming chromosome, which has a diameter of 1400 nm.
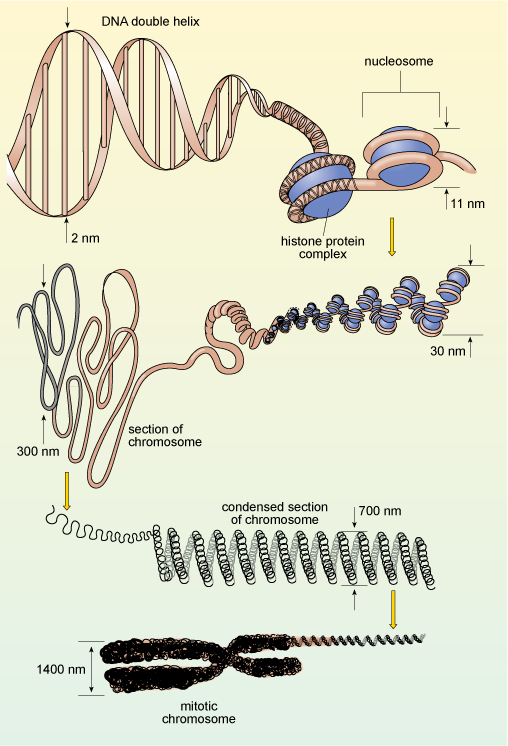
Chromosomes are visible under a light microscope when they are replicating during the metaphase stage of eukaryote cell division.
Now we know the basics of DNA and how it is stored in cells. But how does it carry genetic information? Now we will learn about just that.
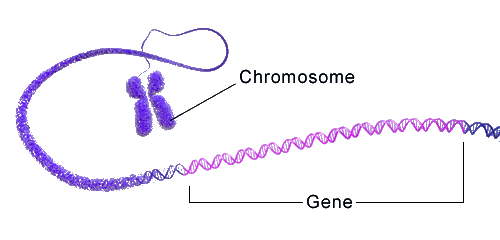
Genetic information is stored in the sequence of bases along a nucleic acid chain. The sequence of nitrogen bases forms genetic codes. Three consecutive bases form a codon. The codon denotes a specific amino acid. In other words, a codon codes a specific amino acid which is the precursor of protein. The whole DNA does not carry the information necessary to make protein. The part of a chromosome which carries information necessary for RNA or protein synthesis is called a gene.
DNA itself is not the template for protein synthesis. The protein-synthesizing machinery lies in the cell cytoplasm while DNA is stored in a safe heaven called nucleus to prevent any damage to the DNA. So an intermediate is used to carry genetic information from the nucleus to cytoplasm. During gene expression, part of the chromosome unwinds it’s coiled structure which makes it possible to make a copy of the information of that particular region. It is called DNA transcription. Through transcription, mRNA (messenger RNA) is formed, which carries the complementary bases of the original gene. Then it goes to the cytoplasm where protein is synthesized with the help of rRNA (ribosomal RNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA) in ribosomes.
This one-way flow of genetic information, from DNA to protein through a two step process by transcription and translation is called the central dogma of molecular biology.
Sources:
- Nucleic Acid Structure. Retrieved from, Chapter 23. Fundamentals of Biochemistry Life at the Molecular Level 5th Edition by Voet & Voet on 04/14/2020
- DNA Replication, Repair and Recombination. Retrieved from Chapter 24. Fundamentals of Biochemistry Life at the Molecular Level 5th Edition by Voet & Voet on 04/14/2020
Subscribe to our newsletter to get more educational content delivered right into your inbox.

